Risky Bulletin Newsletter
August 06, 2025
Risky Bulletin: Russia to designate ERPs as "critical information infrastructure"
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by no-code automation platform Tines. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The Russian government is planning to designate enterprise resource planning (ERP) software as "critical information infrastructure" and require all Russian businesses to migrate to a domestic solution.
The move comes after Russia updated its critical infrastructure law in April this year. The government ordered the operators of all critical infrastructure to migrate to Russian software by September this year.
The government also gave itself the power to designate new items as "critical information infrastructure." This is software large enough to cause nationwide disruptions in the case of a cyberattack, and ERP systems appear to be the first item classified in this new category.
Russian officials have pushed companies to wean themselves off Western-made software and move to domestic alternatives ever since the country's invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
Most of this effort has been through public statements, the foreshadowing of future fines, and projects to finance local alternatives.
While the critical infrastructure law update from April is the first measure that includes a deadline, the previous messaging also worked. According to RBC, most Russian companies use domestic ERPs and have already migrated, and only around a third of all Russian companies still use foreign ERP software, with SAP and Oracle remaining the top platforms.
Most of the Russian companies that migrated are small and medium businesses, which chose the likes of 1C, Galactica, or Turbo ERP.
What still remains using SAP and other foreign ERPs are the larger organizations, which cited the lack of the more sophisticated SAP and Oracle features in domestic alternatives as a reason for their delays.
Representatives say that transitioning their larger companies to Russian alternatives requires more than the ERP itself. This process also involves running the ERP on more powerful database systems and secure operating systems, which also have to be domestic alternatives.
While the Kremlin has pushed the local software sector to create these alternatives, they are far from being the well-tested and well-oiled systems used in the West.
The market for Russian domestic operating systems and database systems is still lagging behind foreign alternatives. This has not impacted SMBs but is still holding back larger Russian corporations from making the move.
Another Vedomosti report last week also cited government sources that a third of Russian companies still used foreign software (not just ERPs).
This is most likely the same upper "third" echelon of the Russian business sector that (still) can't migrate due to the lack of a full Russian software stack and the lack of mature and advanced alternatives for proper feature-to-feature migrations.
Time is running out, though, and the Kremlin is now getting closer to the stage where it starts holding hot coals under the business sector's feet.
Per RBC, these may be a new set of progressive taxes for the companies that don't migrate to a domestic ERP.
Any kind of enforcement or penalty regime will not start in September. Giving your biggest corporations less than four weeks to migrate some of the most complex ERP software, in the middle of August, the typical vacation month, is definitely a dream. This is likely yet another push to get companies to act.
The Russian government is also making other moves. One of these is a new law that introduces the status of "significant" software developer in Russian legislation. It's unclear what this will be used for, maybe some sort of tax deductions, but it's another step the government is taking to cultivate and sustain a self-contained software ecosystem.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Ransomware gang leaks police informant data: Sensitive police data leaked online following a ransomware attack last year. A Louisiana sheriff's office has exposed details on informants, polygraph results, internal affairs investigations, and IMSI catcher warrants. The leak also included training manuals on how to create online sock puppet accounts and how to use Cellebrite and GrayKey phone unlocking tools. The East Baton Rouge Sheriff's Office was hit by ransomware in April last year and had its data leaked after it refused to pay a ransom. [Additional coverage in SAN]
Brosix and Chatox leaks: An unsecured database backup has exposed user personal data and conversations from the Brosix and Chatox messaging platforms.
Chanel data breach: French fashion company Chanel notified customers of a data breach. The incident impacted the brand's US operations. The company said hackers stole data from one of its database providers. It didn't say how many customers were affected. [Additional coverage in WWD]
Cisco data breach: Networking equipment vendor Cisco has suffered a security breach. The incident took place on July 24. Cisco says a threat actor voice-phished a third-party managing its CRM platform. Per unofficial public reports, both Cisco and Chanel had their Salesforce accounts hacked.
Thai hospital gets the dumbest breach fine ever: A Thai private hospital was fined $37,000 for using paper patient records as snack bags. The paper records were found used as wrappings for street food last year. The hospital claimed it used a contractor to dispose of the sensitive records, but failed to follow up. [Additional coverage in the Bangkok Post] [h/t DataBreaches.net]

General tech and privacy
Chrome 139: Google has released version 139 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest change in this release is the distrust of Chunghwa Telecom and Netlock certificates and the end of support for macOS 11, Android Oreo, and Android Pie. There's also a new way for multiple users to work in shared tab groups.
KubeSphere goes commercial: KubeSphere, a cloud OS built around Kubernetes, has stopped development of its open-source codebase and has switched to a commercial licensing scheme.
uBO for Safari: uBlock Origin Lite, today's best browser ad-blocker, is now available for Safari.
SharePoint support is in China: A ProPublica report has uncovered that support for Microsoft's SharePoint software is handled by Microsoft's Chinese engineers. The report comes weeks after security firms accused Chinese state-sponsored hacking units of deploying SharePoint zero-days in attacks.
New WhatsApp anti-scam features: Meta will begin showing warning screens whenever strangers add users to new WhatsApp groups. Group content and notifications will be paused until users can review the group and opt to stay or leave. Meta designed the new feature as one of its anti-scam defenses.

Microsoft Project Ire: Microsoft has unveiled Project Ire, a new AI agent that can help security researchers find new malware.
Perplexity AI violates no-crawl policies: Cloudflare has accused AI company Perplexity of ignoring no-crawl policies. The company allegedly modifies its user agent and changes scanning IPs every time it's blocked by a website. The stealthy Perplexity scans now account for almost a quarter of the company's declared activity.

Government, politics, and policy
AI debacle in Sweden: Swedish Prime Minister Ulf Kristersson is facing a wave of criticism for admitting to using ChatGPT to run the country. This was just too funny not to include. [Additional coverage in The Guardian]
Ohio to approve ransoms in public sessions: Ohio local governments will have to approve future ransomware payments in legislative sessions, in full view of the public. The new requirement was included in the Ohio state budget bill for next year. The same bill will also require all local governments to establish cybersecurity programs to prevent future attacks. [Additional coverage in Cleveland.com]
DHS bans MS-ISAC from cyber grants: The DHS has prohibited state and local governments from using cyber grants on services provided by the Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center. MS-ISAC has provided critical cybersecurity intelligence across state lines and helped secure US elections. The DHS used to provide funding for the group until earlier this year, when it cut all ties under the Trump administration. DHS officials have not explained why they have now effectively banned a former critical CISA partner. [Additional coverage in StateScoop]
It's not hyperbole or exaggeration to say the explicit stance of the Trump administration is explicitly that states' election administrators are not to have dedicated hubs to share cyber threat information, or at least if they are they have to fund such a project completely on their own.
— Kevin Collier (@kevincollier.bsky.social) 2025-08-05T13:24:26.449Z
US explores chip tracking options: The US government is exploring ways to embed location tracking technologies in exported chips. According to Bloomberg, US officials are working with chipmakers on possible technical implementations. The US government aims to prevent the unauthorized flow of advanced technologies to current or future US adversaries.
US Treasury warns of crypto ATMs: The US Treasury Department has urged financial institutions to monitor crypto ATMs and kiosks for suspicious transactions. The Treasury's financial fraud division says the devices are increasingly used for fraud and money laundering. FinCEN says that many ATM and kiosk operators fail to meet anti-money laundering rules as per the Bank Secrecy Act.
National Quantum Cybersecurity Migration Strategy Act: Two US senators have introduced bipartisan legislation to secure federal networks from quantum computing threats. The National Quantum Cybersecurity Migration Strategy Act would require federal agencies to transition networks to quantum-resistant technologies. The effort will be supervised by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy.
New Space Force cyber chief: Charleen Laughlin was appointed as the new deputy chief of space operations for cyber and data for the US Space Force. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
US Cyber Force panel: A special panel was established to put together a roadmap for the creation of a US Cyber Force. The panel is made up of 17 former civilian leaders and retired military brass. Ed Cardon, a former lead for the US Army Cyber Command, and Josh Stiefel, a former staff member on the House Armed Services Committee, are co-leading the panel. According to The Record, the panel will prepare a roadmap for Congress to establish the new Cyber Force branch by next year's NDAA.
The new panel’s “core, ironclad assumption at the outset is that the president has ordered the establishment of the Cyber Force. And then we're going to design it," one of the co-chairs told me in an exclusive interview. therecord.media/panel-to-cre...
— Martin Matishak (@martinmatishak.bsky.social) 2025-08-04T11:14:59.915Z
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Tines Field CISO Matt Muller chats with Casey Ellis about the interesting and out-of-the-box ways they've seen people using the platform. Tines is a platform designed to automate repetitive tasks for IT and security teams. And, as it turns out, it can be used to … gamify shift handover?
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Nigerian scammer extradited: France has extradited a Nigerian man to the US to face charges related to hacking, fraud, and identity theft.
Vishing trend continues: CrowdStrike has published its yearly threat report. Besides the "DPRK workers are everywhere" shtick the company is pushing, another more interesting trend from the report is that vishing continued to be a problem this year again. Several security firms have noted the increase in voice phishing attacks last year, and this has continued this year too, as the technique is extremely good at delivering initial access footholds to threat actors that know how to properly use it.
Innocent Max: Most social media criminal activity in Russia has taken place on Telegram and WhatsApp. The Russian Cyber Police received more than 400 reports of criminal activity on Telegram and another 300 for WhatsApp. No criminal activity has yet been reported on Max, Russia's new national instant messenger. The messenger has only two million users, though.
Cryptodrainer steals $1mil: A threat actor has stolen almost $1 million worth of crypto assets. The attacker used a malicious smart contract disguised as an automated trading bot. The malicious contract emptied the user wallets of all who installed it, according to security firm SentinelOne.
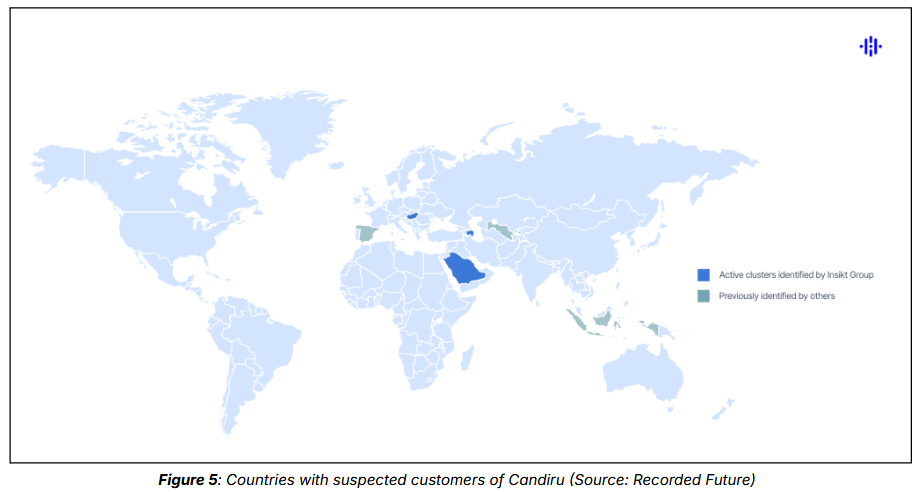
New Candiru infrastructure: Israeli spyware vendor Candiru is still active. Security firm Recorded Future has discovered new server clusters for managing and delivering the company's DevilsTongue spyware. Eight clusters were found, and five are still active. Clusters were found linked to Hungary and Saudi Arabia.
Malware technical reports
SLOW#TEMPEST Cobalt Strike Loader: A security researcher known as dmpdump has published an analysis of the Cobalt Strike Loader used by SLOW#TEMPEST, a group that targets Chinese-speaking users.
Raspberry Robin updates: Zscaler researchers have documented recent changes to the USB-born Raspberry Robin malware.
Akira and Lynx: The Acronis team went looking for code similarities between the Akira and Lynx ransomware, but found that Lynx might be a rebrand of the INC ransomware group.
Interlock ransomware: eSentire has a report out on the Interlock ransomware and its use of ClickFix tactics.
SparkKitty: A campaign leveraging Meta ads is luring mobile users to fake TikTok shops where attackers collect login details and deliver malicious apps. The campaign has used 10,000 fake sites and more than 5,000 malicious Android and iOS apps. The apps shipped with SparkKitty, a mobile infostealer that can steal login credentials and crypto wallet data.
Android SpyBanker: K7 Labs has spotted an Android trojan being spread via WhatsApp as a customer support tool. The app is designed to hijack a device's call functions and redirect all calls through an attacker-controlled number.
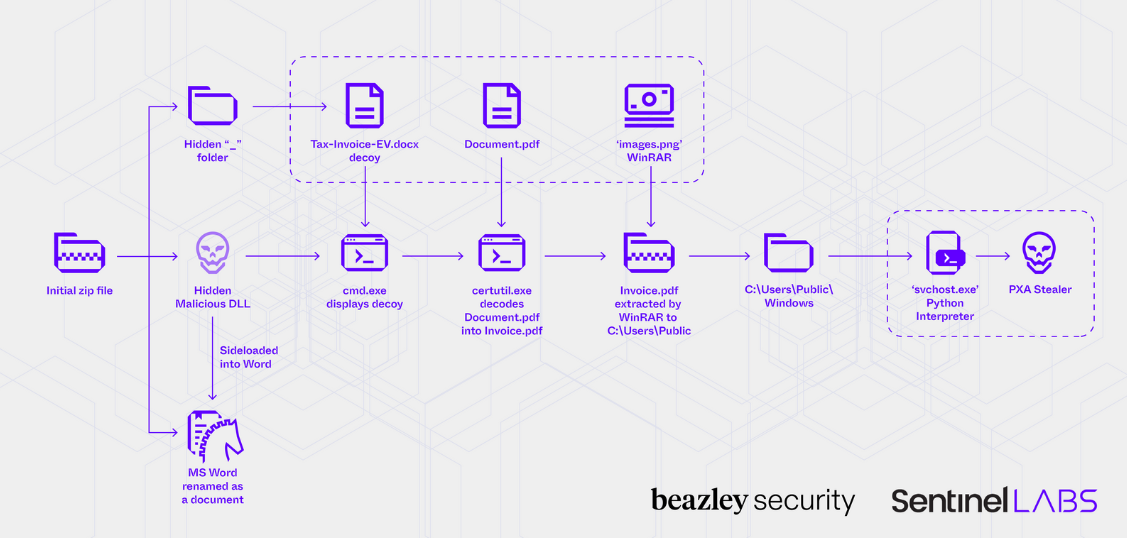
PXA Stealer: SentinelOne and Beazley Security have discovered a new Windows infostealer used in the wild named PXA Stealer, most likely the work of a Vietnamese-speaking cybercrime group.
Sponsor section
In this product demo, CEO Eoin Hinchy shows how Tines' Workbench can integrate an LLM into security workflows to gather, analyze, and act on data from both inside and outside your company. This demo includes grabbing IOCs from an external webpage, comparing them to your company's own incidents, and taking actions like resetting passwords.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
OSS platform abuse: A new Strider report takes a look at recent incidents where foreign state actors tried to weaponize open-source software platforms for espionage attacks.
APT37's RokRAT: South Korean security firm Genians has published a report on RokRAT, one of APT37's favorite malware strains as of late.
UAC-0099: Ukraine's CERT has found new malware used by the UAC-0099 espionage group. These include the MATCHBOIL loader, the MATCHWOK backdoor, and the DRAGSTARE infostealer.
APT36 ops in India: Indian firm CyFirma has published a report on phishing campaigns targeting Indian defense contractors and government entities. CyFirma attributed the campaign to suspected Pakistani group APT36, aka Transparent Tribe.
New Emennet Pasargad rebrand: An Iranian APT group has changed the name of its front company in an attempt to avoid US sanctions. The Cotton Sandstorm group was sanctioned for interfering in the 2020 US presidential election. It operated using the services of a contractor named Emennet Pasargad. The State Department says the company has now changed its name to Shahid Shushtari but still operates from the same address. This is the third time the company has changed its name after also operating as Aria Sepehr Ayandehsazan last year [PDF]. [Additional coverage in Iran International]

IRGC activity during 12-day Israel conflict: SecurityScorecard has published a review of Iran's cyber activities during the recent 12-day armed conflict with Israel. The report has five main takeaways. One of them is below.
"Telegram has emerged as a critical platform for coordination, propaganda dissemination, and command-and-control for both state-aligned proxies and hacktivist collectives. Its perceived anonymity and broad reach make it an attractive medium for these groups to organize, share information, claim responsibility for attacks, and even recruit new members. Monitoring and understanding the activity on such platforms is essential for anticipating and responding to cyber threats originating from these networks."
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
SonicWall warns firewall owners: SonicWall has told owners of Gen 7 firewalls to disable the device's SSLVPN feature due to a security risk. The company says it received reports of attacks against the devices over the past three days from at least three security firms. According to Arctic Wolf, Google Mandiant, and Huntress, attackers hacked SonicWall systems and then deployed ransomware. SonicWall says it's investigating to see if the attacks used older bugs or a new zero-day exploit.
NVIDIA Triton vulnerabilities: Remote attackers can hijack NVIDIA servers running AI models. The attacks are enabled by a chain of three vulnerabilities in the NVIDIA Triton Inference Server platform. The bugs were discovered by Google Cloud's Wiz team in the Triton platform's backend. NVIDIA released security updates this week to patch the issues.
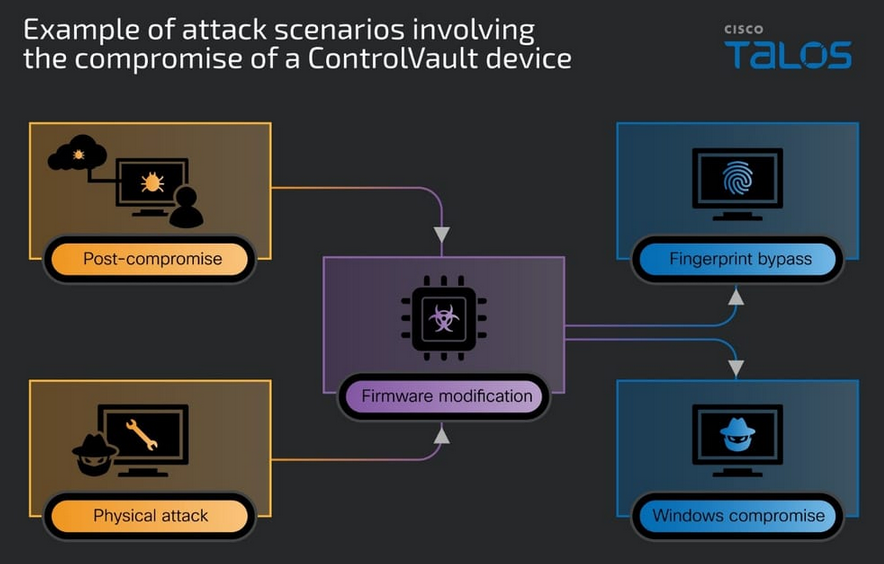
ReVault vulnerabilities: A set of vulnerabilities can allow threat actors to take control of tens of millions of Dell laptops. The bugs impact the ControlVault3 firmware that is used to safely store passwords and biometric data inside a secure chip on Dell Windows laptops. The five bugs, codenamed ReVault, impact more than 100 Dell laptop models. The bugs can be exploited via a Windows API and don't require elevated privileges. Dell has released firmware updates.
MCPoison vulnerability: The Cursor AI-powered code editor has fixed a design flaw in its MCP plugin and integrations engine. The editor failed to monitor for any changes in MCP plugin configurations. Attackers or rogue MCP providers could have modified these files to grant themselves additional code execution capabilities. As part of its update, Cursor will now ask users for re-authorization every time an MCP configuration file suffers the most minor of changes. [Additional coverage in Check Point Research]
Streamlit vulnerability: A vulnerability in the Streamlit app deployment framework can allow attackers to hijack underlying cloud servers. Attackers can exploit a file upload vulnerability to rewrite server files and deploy new SSH configurations. Streamlit released a security patch in March.
Squid RCE: The Squid proxy project has patched a vulnerability that could have leaked server memory. Tracked as CVE-2025-54574, the vulnerability can be used to leak credentials or other sensitive data from the proxy server. Exploitation requires the use of malcrafted Trivial-HTTP responses processed over URN.
BusyBox TOCTOU bug: A security researcher has accidentally published the details of a BusyBox bug that can be abused to crash IoT devices, gain root privileges, or plant persistent backdoors.
NestJS RCE: Socket Security has published a write-up on a complex exploit chain that goes from CSRF to a sandbox escape and then to an RCE vector in the Nest JavaScript framework.
Safari DFG RCE write-up: Exodus Intelligence has published a write-up on a 2024 bug in the WebKit Data Flow Graph (DFG) compiler. The bug (CVE-2024-44308) could lead to remote code execution on Safari by processing malicious web content.
Adobe emergency patches: Adobe has released an out-of-band security update to patch two vulnerabilities in the form builder for its Experience Manager CMS. It released the patches after security researchers published proof-of-concept code online. The researchers published the code after Adobe failed to patch the issues in a 90-day time window. Adobe said the bugs were not exploited in the wild at the time of the patch.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with three vulnerabilities that are currently exploited in the wild. All three are old D-Link security camera bugs from 2020 and 2022.
Android Security Bulletin: Google has released the Android security updates for August 2025. Six issues were patched this month.
Big Sleep awakens: Google's Big Sleep AI vulnerability scanner filed its first 20 bug reports.
Today as part of our commitment to transparency in this space, we are proud to announce that we have reported the first 20 vulnerabilities discovered using our AI-based "Big Sleep" system powered by Gemini — goo.gle/bigsleep
— Heather Adkins (@argv.bsky.social) 2025-08-04T15:24:27.505Z
Zero Day Quest 2026: Microsoft will be offering a $5 million prize pool for its Zero Day Quest AI hacking contest next year.
Microsoft bug bounty program: Microsoft has awarded $17 million to security researchers for bugs reported through its official bug bounty program. The funds went to 344 researchers from 59 countries across the globe. The largest award was $200,000. The sum is close to what Microsoft paid the year before.

Infosec industry
Acquisition news: SentinelOne has acquired AI security firm Prompt Security.
Easterly joins Huntress: Former CISA Director Jen Easterly has joined the advisory board of security firm Huntress. [Additional coverage in Axios]
New tool—MSSQLHound: Security firm SpecterOps has released MSSQLHound, a tool for mapping MSSQL attack paths to BloodHound.
New tool—EntraGoat: Security firm Semperis has released EntraGoat, a deliberately vulnerable Microsoft Entra ID infrastructure designed to simulate real-world identity security misconfigurations and attack vectors.
New tool—scepreq: Security researcher Dirk-jan Mollema has open-sourced scepreq, a tool to talk with AD CS NDES servers over the SCEP protocol and request certificates.
BSides LV 2025 videos: Live streams from the BSides Las Vegas 2025 security conference, which is taking place this week, are available on YouTube.
Threat/trend reports: CrowdStrike, CyberProof, IANS+Artico, Netskope, Red Canary, SixMap, and Strider have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq dissect the Belarusian Cyber Partisans hack of Russian airline Aeroflot. Despite the short-term impact, the airline will likely bounce back quite quickly. But it is still a big win for the Cyber Partisans.
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about how the recent SharePoint exploitation is a blow-by-blow repeat of the 2021 Microsoft Exchange mass compromise event. The international response to that clearly didn't deter Chinese hackers, so it is time to try something different.
