Risky Bulletin Newsletter
June 02, 2025
Risky Bulletin: Law enforcement take down AVCheck
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by asset inventory and network visibility company runZero. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Law enforcement agencies from Finland, the Netherlands, and the US have seized AVCheck, an underground service used by cybercriminals.
The service has been around for over a decade and allowed malware developers to test their code against major antivirus engines and malware scanners.
It ran the engines and scanners in isolated cloud environments that cut off telemetry and prevented them from phoning back home to the security firms with warnings when malware was detected.
Threat actors bought subscriptions on AVCheck, uploaded their payloads, fine-tuned the malware code until it wouldn't trigger any detections, and then deployed it in real attacks, knowing it wouldn't be spotted until it was too late.
Called a Counter AntiVirus (CAV) by security professionals, the site was one of several of its kind that exist online and are a big part of the underground cybercrime ecosystem.
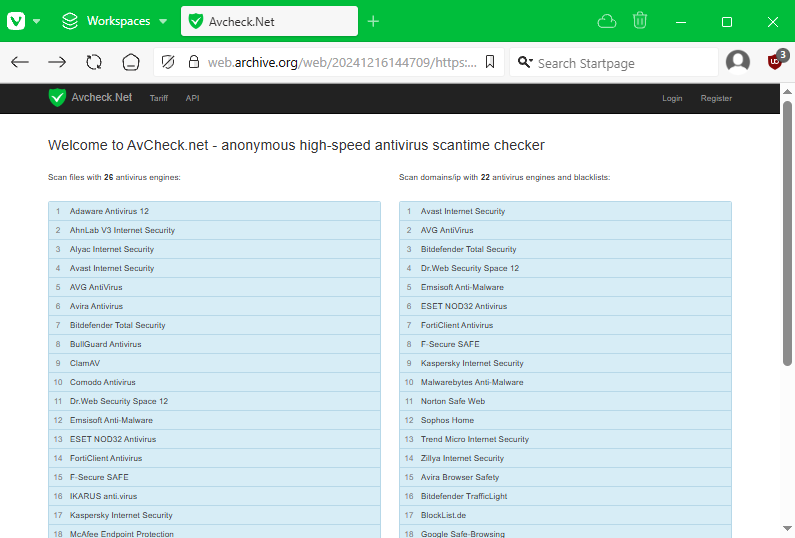
Officials seized AVCheck[.]net and four other domains—Cryptor[.]biz, Cryptor[.]live, Crypt[.]guru, and Getcrypt[.]shop—which provided "malware crypting" services.
These latter two were also managed by the AVCheck admins and allowed malware authors to scramble and obfuscate a payload's source code to improve its chances of evading detection.
In a message on their Telegram channel, the AVCheck admins said the services were down "due to unforeseen circumstances."
Dutch police claim that prior to the takedown, they ran a fake login page on AVCheck, collected data on users, and warned them about using the service.
Officials said the takedown was part of Operation Endgame, a law enforcement operation that began last year and specifically targets cybercrime services. So far, the operation has taken down seven malware botnets used for initial access into corporate and government systems.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
White House investigates Wiles hack: Unidentified individuals have contacted Republican lawmakers and businesspeople over the past weeks, posing as White House chief of staff Susie Wiles. The intruders allegedly used deep fake technology to pass as Wiles herself. The White House official said the attackers hacked her phone contacts—but it's unclear if they hacked her phone or an online account. Federal investigators told the WSJ they don't believe a foreign nation was involved. [Additional coverage in the WSJ]
IIJ breach: Japanese telco IIJ says hackers stole the email data of over 4 million customers last year. The ISP is one of the several Japanese companies that have been hacked using an Active! Mail zero-day. [Additional coverage in Piyolog]
BitMEX failed hack: The BitMEX cryptocurrency exchange says it detected and stopped an intrusion attempt from North Korean hacking group Lazarus. BitMEX's security team gained access to one of the group's servers and traced one of its operators to Jiaxing, China. The company spotted the attempted hack after a Lazarus operator tried to lure one of its developers into running a malicious GitHub project.
General tech and privacy
Opera Neon: Opera has released Neon, an "AI browser." The browser is infused with all kinds of agentic AI integrations and is available under a subscription model.
Chrome distrusts two CAs: Google will distrust TLS certificates issued by certificate authorities Chunghwa Telecom and Netlock. Certificates will be removed from Chrome and ChromeOS in version 139, expected to be released at the end of July. Google said it removed the companies from the Chrome root store because it lost confidence in the two due to incidents over the past year.
Linux kernel now supports hardware-wrapped encryption keys: The Linux kernel has added support for a new security feature named hardware-wrapped inline encryption keys. The feature stores encryption keys inside secure hardware components and prevents them from appearing in plaintext in system memory. The feature was initially developed for Android to block cold boot attacks. It has now shipped with the Linux kernel v6.16 (which also adds support for confidential computing).
Microsoft Entra to support TLS inspection: Microsoft has added support (still in preview, though) for TLS inspection to its Entra Internet Access secure web gateway service.
Google Meet to replace Duo: Google Meet will fully replace the legacy Google Duo calling feature in September, finishing the product's full deprecation. [Additional coverage in 9to5Google]
New DRMs needed: An Ember Analytics report concludes that video piracy is at an all-time high and that new DRMs are needed.
Government, politics, and policy
Senators ask for CSRB back: Four Democrat senators have asked DHS Secretary Kristi Noem to reinstate the Cyber Safety Review Board (CSRB). The Board was established in 2022, investigated serious cybersecurity breaches, and made recommendations to government agencies and the private sector. It was dismissed days after President Trump took office this year.
EU age-verification app: The EU is launching a new age-verification app in July. The app will focus on privacy and confirm a user's age without disclosing their personal data to tech platforms. The move comes as several member states are pushing to implement an EU-wide minimum age to use social media. [Additional coverage in the Identity Week]
Thailand blocks five crypto exchanges: The Thai government says it will block access to Bybit, CoinEx, OKX, 1000X, and XT.com after the five companies failed to register in the country. [Additional coverage in CoinDesk]
Israel's vague threat to Spain: An Israeli official issued what could be categorized as a veiled threat to Spain, hinting that his government has not yet looked into Spain-related data collected by NSO Group through the Pegasus spyware. The spyware was allegedly used both by and against the Spanish government. Israel and Spain are at political odds after Spain recognized Palestine as a state last year. [Additional coverage in El Espanol]
Israel thwarts cyberattacks linked to assassinations: Israel's Shin Bet intelligence agency says it thwarted 85 Iranian cyber operations this year designed to gather intelligence for top-level assassinations. The cyberattacks sought to gather data on senior Israeli security officials, politicians, journalists, and academics. Targets were invited to Google Meet conferences, where operatives tried to obtain info on their home addresses and personal routines. That information would then be handed to operatives on the ground in Israel. [Additional coverage in Iran International]
FSB to hold an infosec conference: The FSB, through its NKTsKI division, will hold a yearly infosec conference going forward, dedicated mainly to cyber defense. [h/t Oleg Shakirov]
Sponsor section
In this sponsored interview, Risky Business Media’s brand new interviewer Casey Ellis chats with runZero founder and CEO HD Moore about why vuln scanning tech is awful and broken. He also talks about how they’re trying to do something better by glueing their own discovery product to the nuclei open source vulnerability scanner.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Germany identifies TrickBot leader: German authorities have identified the leader of the TrickBot cybercrime gang as a 36-year-old Russian named Vitalii Nikolaevich Kovalev. He operated inside the gang under the pseudonyms of Bentley and Stern. Kovalev was charged and sanctioned by the US in 2023 for his role in the group but was never identified as its main administrator. The TrickBot botnet went through two takedowns, one in 2020 and a second one last year.

New npm malware: One hundred eighty-nine malicious npm packages were discovered and taken down last week. Check out the GitHub security advisory portal for more details.
Malicious PyPI packages: Researchers at Safety CLI have found 11 Python libraries on PyPI that targeted Solana crypto developers and attempted to steal source code and Jupyter Notebook data.
Malicious infrastructure: Intrinsec researchers have linked two UK ASes to bulletproof hosting provider BtHoster.
New DataCarry ransomware gang: A new ransomware operation named DataCarry launched last week. Its dark web leak site currently lists nine victims.
Meta ad scam landscape: AI Forensics has published a 30-page report on Meta's failure to moderate its advertising platform. The report specifically looks at all the health-related ads and all the scams they carry, from unapproved drugs to deceptive health claims.
"Using Meta's Ad Library data, we identified over 46,000 advertisements containing unapproved drugs and deceptive health claims that appeared on European users' screens over 292 million times. These ads violated at least 15 of Meta's own Advertising and Community Standards, featuring celebrity deepfakes, impersonation of medical professionals and news outlets, and misleading health claims."
Lumma Stealer infrastructure is returning online: The developers of the Lumma Stealer malware are making "significant efforts" to restore servers and return online. The malware has been down since May 21, when law enforcement seized almost three-quarters of its infrastructure. Despite the efforts, Check Point researchers say the operation suffered "significant reputational damage," and threat actors are not hurrying back.
Haozi PhaaS returns: Netcraft has spotted new activity from Haozi, a PhaaS operated by a Chinese-speaking threat actor.
Malware technical reports
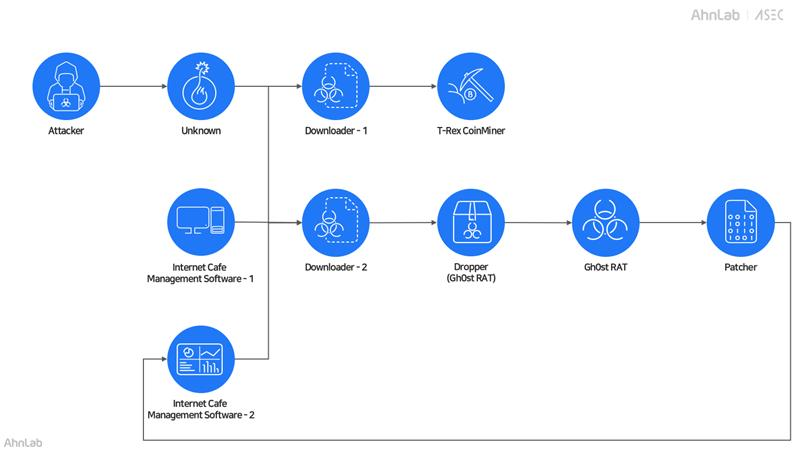
T-Rex cryptominer: Internet cafes in South Korea have been infected with cryptocurrency miners in what appears to be a well-organized campaign. The point of entry for the infections is still unknown, but the hackers are using the cafes' management platform to spread the T-Rex cryptominer to all PCs. The threat actor behind the attacks has been active for three years, according to a report from local security firm AhnLab.
Sponsor section
Senior Sales Engineer Ali Cheikh demonstrates runZero to Risky Business host Patrick Gray. runZero is a cyber asset management tool that combines active scanning, passive discovery, and API integrations to discover IT, OT, and IoT assets (both managed and unmanaged) across your network, including cloud, mobile, and remote environments.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Patchwork and DoNot connections: Chinese security firm QiAnXin looks at some of the connections between Patchwork and the DoNot Team, two Indian APT groups.
BO Team profile: Russian security firm Kaspersky has published a profile on Ukrainian hacking group BO Team, also tracked as Black Owl, Lifting Zmiy, and Hoody Hyena. The group has a history of destructive and data-encryption attacks targeting Russian companies. The report highlights the group's isolation within the pro-Ukraine hacktivist space, where it doesn't coordinate, communicate, or share tools with other groups.
GRU Unit 29155 profile: The Insider has published a profile of GRU Unit 29155, an elite GRU unit responsible for hacks, disinformation, and sabotage across Europe. Their hacking unit is known in infosec circles as Ember Bear, Cadet Blizzard, Frozenvista, UNC2589, and UAC-0056.
TikTok info-ops summary: TikTok has published its monthly report on covert influence operations the company has spotted on its platform in April this year. The company took down influence networks targeting political discourse in the Philippines, Indonesia, Iraq, Romania, Poland, and Hong Kong.

Meta disinfo ops: Meta has published its Adversarial Threat Report for the first quarter of the year. The company took down disinformation ops operating out of China, Iran, and Romania. [Additional coverage in Meta's Q1 2025 Adversarial Threat Report/PDF]
ChatGPT starts returning Russian disinfo: ChatGPT has been observed reproducing Russian propaganda from a pro-Kremlin network named Pravda. The incidents come after researchers warned that Pravda was laying the groundwork for having its propaganda indexed by AI assistants. The most recent of these warnings came a week ago. The group has been posting large quantities of English-language fake news on Russian social media network VK, where it can't be taken down but from where it's automatically picked up by AI training systems.
Matryoshka leaves BlueSky for TikTok: Russian disinformation group Matryoshka has stopped posting on BlueSky and moved to flood TikTok with pro-Kremlin propaganda. The group has been historically active on Twitter and started posting on BlueSky last December. The switch took place last week as part of a campaign targeting Moldova and its pro-EU President Maia Sandu. Researchers say that prior to the group's move, TikTok saw almost no posts discussing Maia Sandu over the past three months—confirming again that most political activity on TikTok originates from info-ops.
3/9 Why we believe they started TikTok only yesterday? We could not find similar TT posts / accounts related to Moldova / Sandu for 3 months to date. While on X and BlueSky, 🪆 is for over 6 weeks now running a smear campaign targeting Maria Sandu: bsky.app/profile/anti...
— antibot4navalny | bot blocker | блокировщик ботов (@antibot4navalny.bsky.social) 2025-05-30T23:55:04.955Z
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Azure Arc as a C2: Security researcher Andy Gill shows how threat actors could abuse the Azure Arc service as a command and control system for their operations.
Lovable platform leak: A vulnerability in the Lovable AI-based software-building platform is leaking sensitive information from the company's customers. Attackers who can identify customer databases can send specially crafted requests that expose their content, such as user personal data and API keys. Engineers from both Replit and Palantir have independently found the same issue and retrieved data from apps developed with Lovable. Details about the bug were published online last week after the company failed to patch the issue for over two months.
vBulletin exploitation: Hackers are exploiting two recently disclosed vulnerabilities to take over vBulletin forums. The two bugs were patched in April last year, but attacks began last week after security researcher Egidio Romano published details and proof-of-concept code. Attacks were first spotted by Ryan Dewhurst, the administrator of KEVIntel.
Linux bugs: Qualys researchers have found an info disclosure in the systemd-coredump process that can be used to leak password hashes.
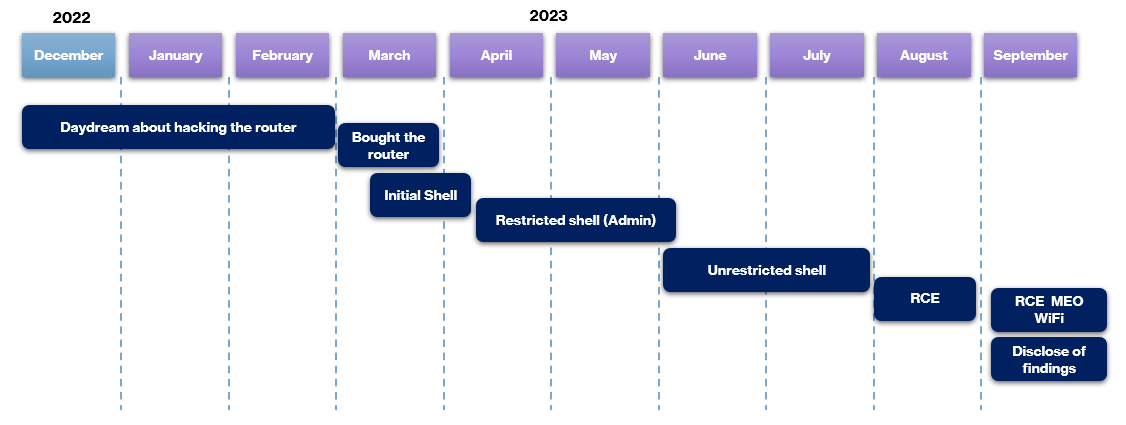
FiberGateway exploit: Security researcher João Domingos has published details about an RCE chain in FiberGateway GR241AG, a router model widely used by Portuguese ISP Meo.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Delinea, Ender Analysis, Kaspersky, Meta, and Ox Security have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Acquisition news: Vulnerability management platform Tenable has acquired AI attack surface startup Apex Security.
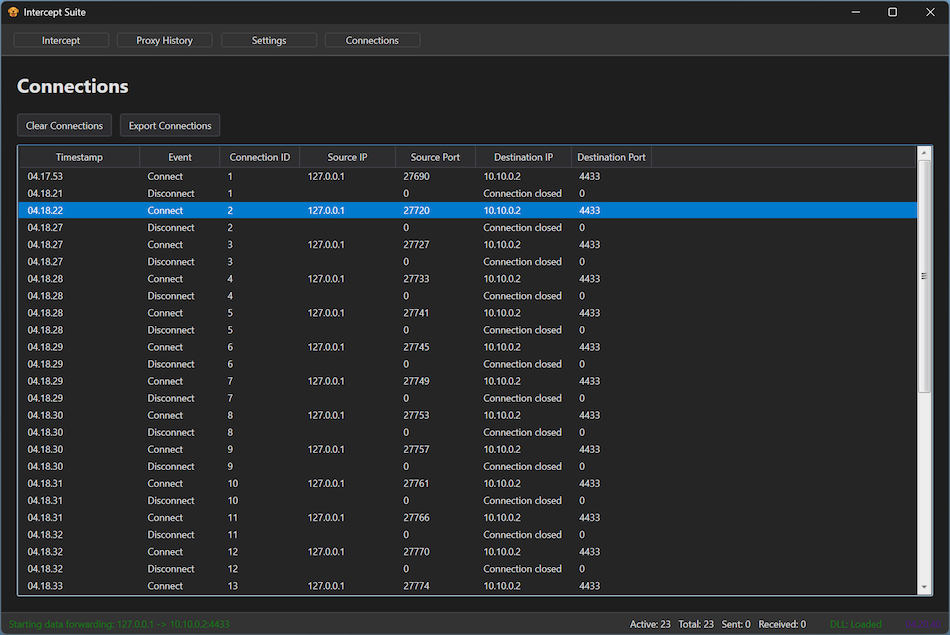
New tool—InterceptSuite: Security engineer Sourav Kalal has released InterceptSuite, a tool to intercept and analyze network traffic in Windows applications.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about Russian DanaBot malware developers making a tailored variant of their malware specifically for espionage. This fills in some of the blanks on the exact relationship between Russian criminals and the country's intelligence services.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about cyber's 'hard problems' and why they are intractable.
