Risky Bulletin Newsletter
October 29, 2025
Risky Bulletin: HackingTeam successor linked to recent Chrome zero-days
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by Knocknoc. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The company that formed from the remnants of Italian spyware vendor HackingTeam is now allegedly involved in hacking all sorts of private and public sector targets in Belarus and Russia.
Memento Labs has targeted media outlets, universities, research centers, government organizations, financial institutions, and other organizations.
The company operates a spyware platform named Dante, through which it deploys infrastructure, exploits, and its final payload—the LeetAgent implant/agent.
Russian security firm Kaspersky says it detected the company's operations earlier this year and traced operations back to 2022.
This year's attacks involved the use of a Chrome zero-day (CVE-2025-2783), suggesting the company has rebuilt its zero-day and exploit inventory since its disintegration in the mid-2010s.
The attack chain involved phishing emails with links to malicious pages hosting the zero-day's exploit. The zero-day allowed malicious code to escape Chrome's security sandbox and then run malicious code with the help of a second exploit.
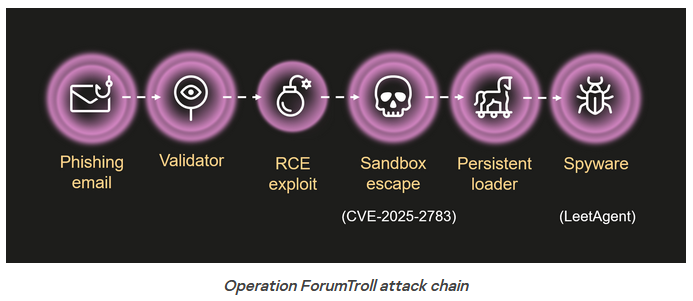
Back in March, Kaspersky described the attacks as "highly sophisticated." In a new report this week, Kaspersky provided more details about the attacks, which also involved highly volatile server infrastructure that confirmed the actual victims were clicking the link and then disappeared once the target landed on the exploit delivery page. This is operational security that is rarely seen in APT operations.
The phishing emails were also not your regular slop and actually used carefully crafted Russian text. Kaspersky's Boris Larin explains:
"The malicious emails sent by the attackers were disguised as invitations from the organizers of the Primakov Readings scientific and expert forum. These emails contained personalized links to track infections. The emails appeared authentic, contained no language errors, and were written in the style one would expect for an invitation to such an event. Proficiency in Russian and familiarity with local peculiarities are distinctive features of the ForumTroll APT group, traits that we have also observed in its other campaigns. However, mistakes in some of those other cases suggest that the attackers were not native Russian speakers."
Despite its pretty comprehensive report on this campaign, Kaspersky says they still have a limited view of Memento Labs operations, since they have not been able to retrieve any of the Dante platform modules.
The group's operations have been traced back to 2022, the year of Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and Kaspersky says the attacks are clearly espionage-related, but Kaspersky has not gone as far as to attribute any of the operations to any specific country (or military organization, wink-wink).
But Memento Labs operations have been spotted all over Russia, and haunted multiple local security vendors. Dr.Web spotted one of Memento Labs' phishing operations in September 2024. F6 tracks past attacks as the Dante APT. Positive Technologies initially tracked the group as TaxOff and Team46, before linking the two operations once Kaspersky's ForumTroll report came out in March.
A bigger picture is slowly being assembled, of a persistent and very endowed attacker capable of targeting Russian-speaking users with extreme precision and success.
Earlier research on the same threat actor that used Dante reported today by Kaspersky Dr. Web first found malware w/ the DANTEMARK label st.drweb.com/static/new-w... F6 called it Dante APT www.f6.ru/cybercrime-t... PT linked ForumTroll w/ a few other clusters global.ptsecurity.com/en/research/...
— Oleg Shakirov (@shakirov2036.bsky.social) 2025-10-27T19:54:46.142Z
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
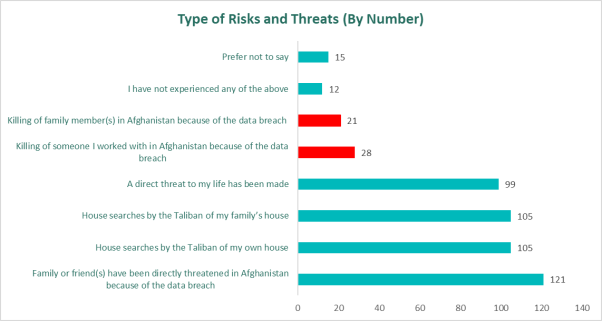
People died after the MoD Afghan leak: Forty-nine Afghans lost family members or colleagues following a leak at the UK Ministry of Defense. The UK government exposed the details of 19,000 Afghan citizens who helped the UK military during the Afghan war. Forty percent also said they received death threats from the Taliban after the UK government exposed their data in February 2022. Others also reported beatings and torture. [Additional coverage in Arab News]
F5 breach to slow company growth: American tech company F5 expects revenue growth to slow over the next two quarters following a recent security breach. F5 CEO Francois Locoh-Donou told shareholders the company has to increase investments in its internal cybersecurity. The company disclosed a breach earlier this month. Suspected Chinese state-sponsored hackers breached F5's network in late 2023 and stole source code and vulnerability reports. [Additional coverage in Axios]
GCash data breach: Philippine authorities are investigating a possible breach of mobile payments service GCash. The company's data was allegedly posted on a dark web hacking forum over the weekend. It included account numbers, customer names, and other KYC records. GCash said it was aware of the forum post but did not confirm a breach. [Additional coverage in the Philippine News Agency]
Svenska Kraftnät hack: Hackers have breached servers operated by Svenska Kraftnät, Sweden's state-owned power grid operator. The breach impacted file-sharing servers, and the incident didn't impact electricity supply operations. The Everest ransomware group took credit for the attack. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Conduent incident: In breach filings, government technology contractor Conduent said a breach it disclosed in January this year began in October of last year.
US city paid ransomware: The city of Gloversville, New York, fell victim to a ransomware attack in March and paid hackers $150,000 to restore its network. [Additional coverage in News10]
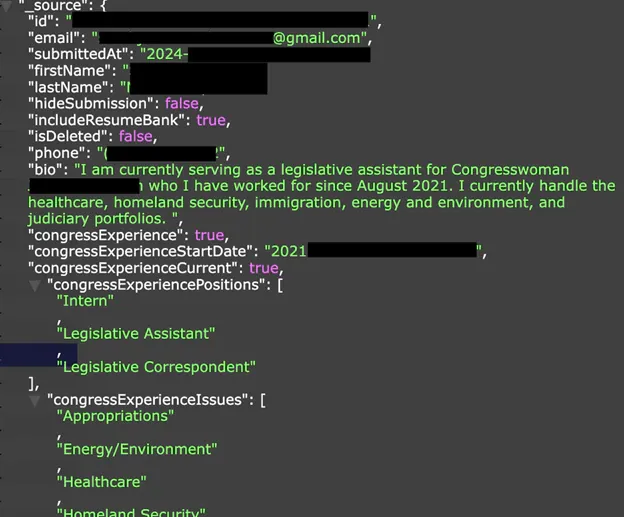
Leak at the House Democrats: A misconfigured database has leaked the resumes of people who applied for jobs with the US House Democrats. More than 7,000 individuals were affected. The leak was traced back to a resume bank, a server where resume submissions are stored. According to Safety Detectives, the database did not have a password or encrypt its data.
General tech and privacy
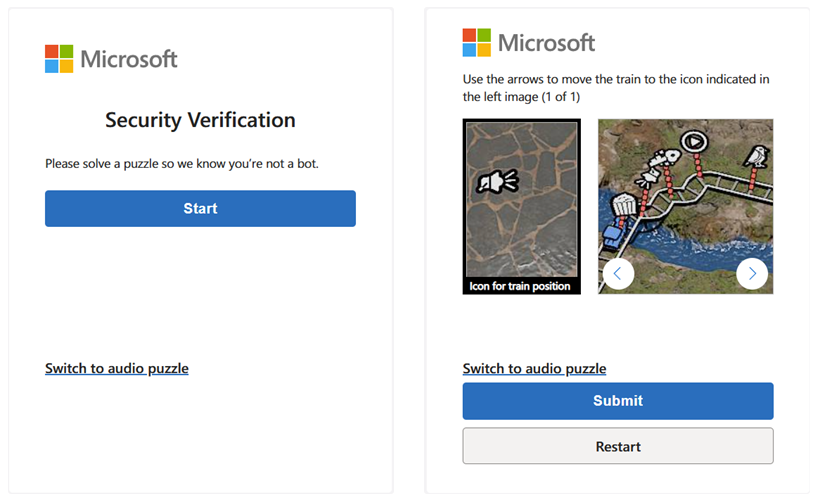
Azure gets its own CAPTCHA: Microsoft has added a CAPTCHA feature to its Azure FrontDoor web firewall product. This is what 99% of Starlink users will be solving in the coming months. Good luck!
Swift for Android: Apple has released the first preview version of Swift for Android. The language was designed to allow developers to code Android apps in the Swift programming language.
Twitter to prompt users to re-enroll security keys: X is retiring its old twitter.com domain. The company will prompt users to re-enroll their security keys over the coming two weeks. Users who don't update security keys by November 10 will have their accounts locked.
Microsoft Store bloatware: Microsoft will let admins remove pre-installed Microsoft Store apps.
Australia sues Microsoft: Australia's consumer watchdog has sued Microsoft for trying to mislead Australians to pay more for their Microsoft 365 due to its new (nobody-asked-for) AI features. [Additional coverage in The Guardian]
Clearview AI criminal complaint: Privacy group noyb has filed a criminal complaint against facial recognition company Clearview AI and its management. Noyb claims the company ignored GDPR fines in five countries and continued to operate despite injunctions and privacy regulations. Clearview has scraped billions of photos of EU citizens without their permission and used the data for a facial recognition product sold to law enforcement agencies.
Musk launches Grokipedia: Elon Musk has launched Grokipedia, his lame attempt at Wikipedia, written by the Grok AI and full of articles copied from the real Wikipedia.
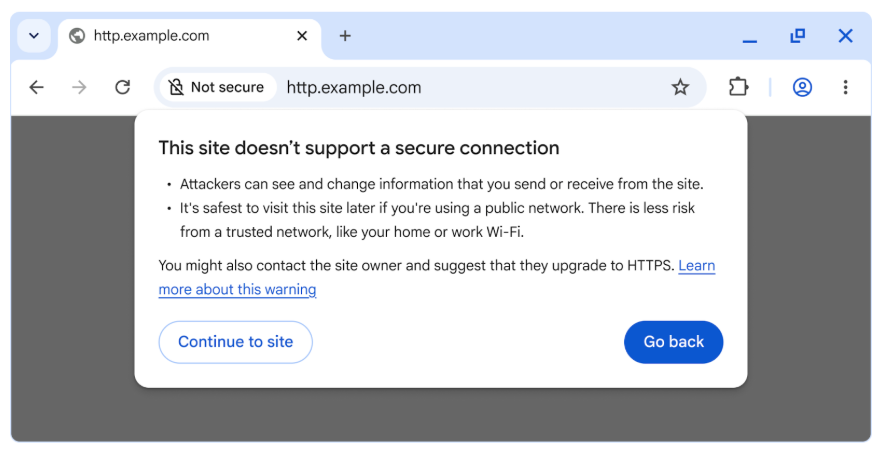
Chrome will go HTTPS by default next year: Google Chrome will load all websites via secure HTTPS connections starting in October of next year. The browser will prompt users every time they try to load a website via an insecure HTTP connection. The change will happen with the release of Chrome version 154. Google says 95% of all Chrome traffic already takes place via HTTPS.
Government, politics, and policy
Europol calls for caller ID spoofing countermeasures: Europol has asked governments to work together on measures to prevent caller ID spoofing. International traceback mechanisms are needed to track down and identify the origin of spoofed calls. The information should be used by telcos to block spoofed calls, which are often used for fraud and scams.
Trump nominates cyber guy for Coast Guard chief spot: The White House has nominated a former leader of the Coast Guard Cyber Command to be the branch's next top commander. Admiral Kevin Lunday was commander of the Coast Guard Cyber Command between 2016 and 2018. He has been acting Coast Guard commander since January 21, after Donald Trump took office again, and was expected to receive the job. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Patrick Gray chats with Knocknoc CEO Adam Pointon about why true Zero Trust architectures never really got there. Spinning up ZTNA access to core applications and slapping SSO prompts on everything else is great, but if we're honest, it's not really Zero Trust. So, how and why did we get here?
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Fifteen to plead guilty in Italy hacking mega-scandal: Fifteen individuals are expected to plead guilty this month in Italy to a complex hacking and extortion scheme. The individuals worked for Equalize, an Italian company that hacked government databases to create dossiers on the country's elite. Italian police discovered the scheme while monitoring a mafia member, who was using the company's data for ransoms. Authorities arrested four in October of last year. The scheme was led by a former police inspector, Carmine Gallo, who passed away from a heart attack this March. [Additional coverage in Politico]
More SMS blaster arrests in the Philippines: The Philippine National Police arrested two suspects last week for driving around the country's capital with SMS blasters. They sent SMS spam posing as telcos in Manila's financial district and popular malls. The two men didn't know each other, but police say they received orders from the same Chinese boss. [Additional coverage in CommsRisk]
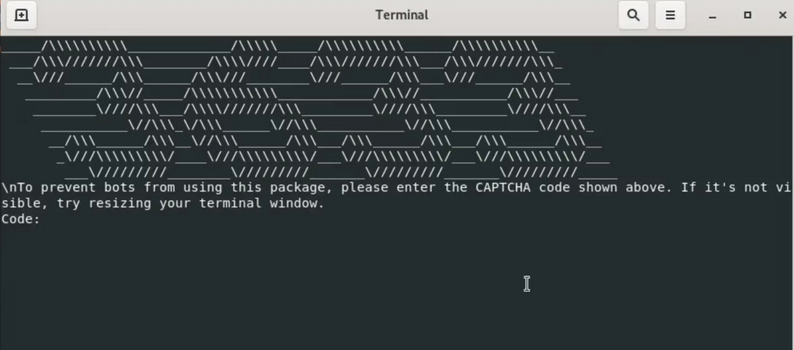
npm malware with CLI CAPTCHA: Socket Security has spotted 10 malicious npm packages. The thing that stands out about them is the use of a CAPTCHA challenge in the npm CLI as they're being installed, most likely as a fake-out to convince victims they're installing a legitimate and actively maintained package. The final payload is an infostealer.
Siberislam (Mutarrif) profile: Nordic Monitor has published a profile on Siberislam (or Mutarrif), the hacktivist group that defaced the flight boards at several airports across North America this month. The publication has linked the group to the Islamic Great East Raiders Front (IBDA-C), an extremist group in Turkey tolerated by the local government and with links to al-Qaeda.
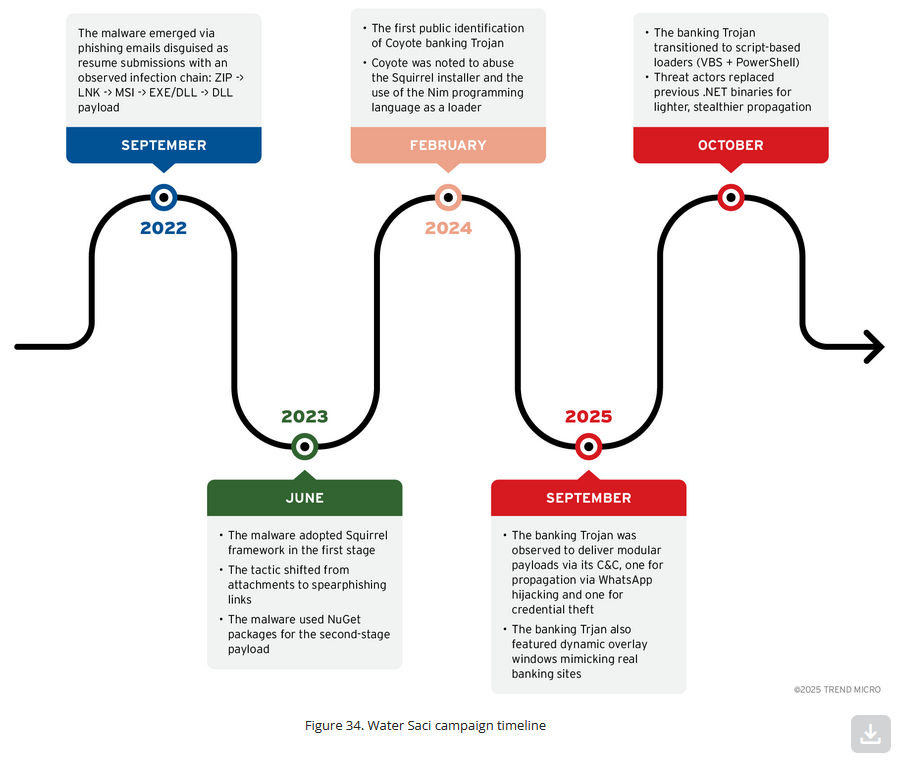
Water Saci possible links to Coyote: Trend Micro has discovered possible links between Water Saci, a group behind a WhatsApp worm targeting Brazilian users, to the developers of the Coyote banking trojan, which was also spread via WhatsApp and targeted Brazilian users last year.
Malware technical reports
GhostGrab: CyFirma researchers have spotted GhostGrab, a new Android banking trojan that also dabbles in info-stealing and cryptomining.
Herodotus: Mobile security firm ThreatFabric has discovered a new Android banking trojan named Herodotus. The company believes the malware may be linked to the old Brokewell trojan. The trojan also has a smart feature that introduces random delays between text entered inside text fields to make it look like a human is typing. This is to defeat some online banking anti-fraud detection features.
Atroposia: Varonis has spotted a new RAT named Atroposia offered through a MaaS model. A unique feature is a built-in vulnerability scanner to search for ways to move laterally.
Midnight decrypter: Avast has released a free decrypter to allow victims of the Midnight ransomware to recover their files without paying the ransom. The ransomware was coded on the source code of the older Babuk ransomware. Avast says changes made to the old Babuk code introduced bugs that allowed the decryption.
Trigona ransomware: AhnLab looks at recent attacks of the Trigona (Mimic) ransomware gang against MSSQL databases.
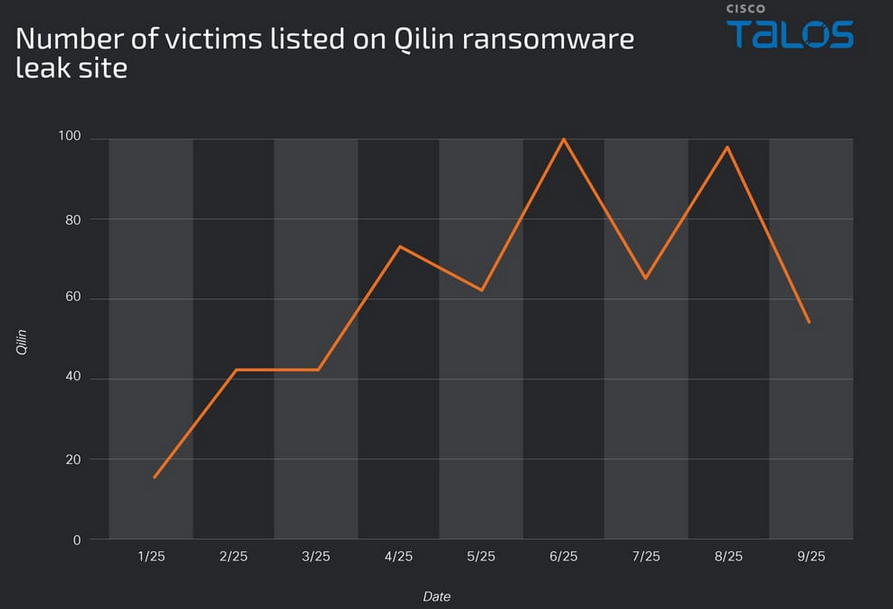
Qilin tactics: Cisco Talos has published a report on the various techniques it saw Qilin and its affiliates use in recent intrusions. The group has been the year's most active ransomware operation.
Sponsor section
In this sponsored product demo, Knocknoc CEO Adam Pointon walks Patrick Gray through the Knocknoc secure access platform. Knocknoc is a platform that restricts network and service availability to authenticated users via existing network security equipment. Users don't need to install an agent. It also has an identity-aware proxy component that supports web applications and RDP.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
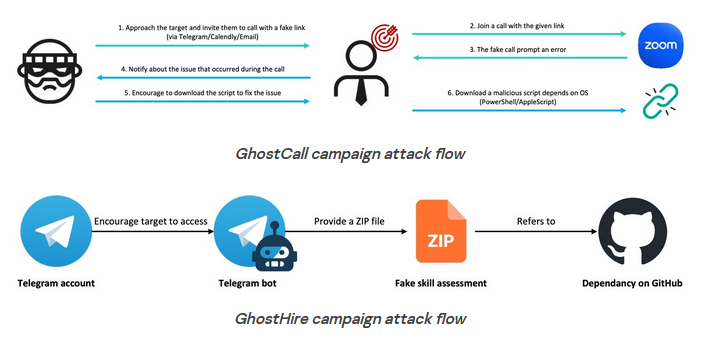
GhostCall and GhostHire: Kaspersky has published a new report on the activities of North Korean hacking group BlueNoroff. The report covers GhostCall and GhostHire, two operations that target the cryptocurrency ecosystem using fake business meeting invitations and fake job openings.
"Our research indicates a sustained effort by the actor to develop malware targeting both Windows and macOS systems, orchestrated through a unified command-and-control infrastructure. The use of generative AI has significantly accelerated this process, enabling more efficient malware development with reduced operational overhead."
KittenBusters, episode 4: The KittenBusters group has leaked new documents related to the operations of Iranian cyber-espionage group Charming Kitten (APT35). The new files include the group's financial and budgeting documents. The files expose Bitcoin payments for domains and servers, ProtonMail accounts, and connected shell companies. According to Iranian cyber activist Nariman Gharib, the group's entire operation runs on only around $10,000. A previous leak also linked the group to the Shuhada IRGC base in Tehran.
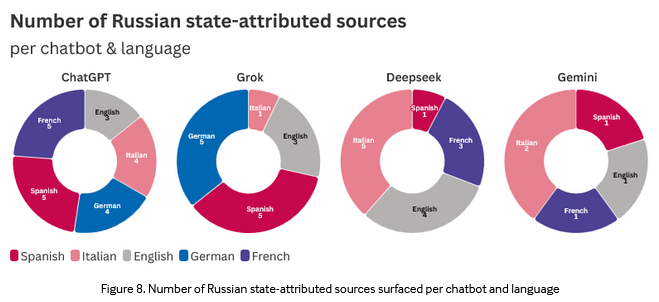
Russian disinfo in AI chatbots: Four popular chatbots are returning Russian state propaganda on topics related to the war in Ukraine. The Institute for Strategic Dialog ran 300 queries in five languages against ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok, and DeepSeek. The ISD says the chatbots returned Russian propaganda for 18% of queries. The report's findings are identical to similar research published by the American Sunlight Project, NewsGuard, and Open Measures.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
XWiki exploitation: Threat actors are exploiting a vulnerability in the XWiki enterprise platform to deploy cryptominers. Tracked as CVE-2025-24893, the vulnerability is an unauthenticated, remote template-injection bug that was patched back in February. Security firm VulnCheck says it detected the attacks against its XWiki canaries.
New DELMIA exploitation: Hackers are exploiting two recently patched vulnerabilities in the DELMIA Apriso factory management platform. Attacks began a month after the bugs were patched and disclosed at the end of September. They are the second batch of DELMIA bugs exploited this year (after a first one in September).
Unpatched WSO2 vulnerabilities: Cloud software provider WSO2 has failed to patch almost a dozen vulnerabilities in a common codebase used by multiple of its products. French security firm Lexfo says the bugs include an assortment of issues ranging from remote code execution attacks to CSRF and SSRF issues. WSO2 patched only one bug, an authenticated RCE against the Siddhi SQL component (CVE-2025-5717). Lexfo has released proof-of-concept code for many of the unpatched bugs.
Old Bluetooth bugs: Synacktiv has published a technical write-up on a 2023 Bluetooth vulnerability (CVE-2023-40129) patched in the Android OS. This was a zero-interaction, no-auth command execution via Bluetooth's GATT protocol.
macOS bugs write-up: Karol Mazurek has published a write-up on two macOS bugs for LPE (CVE-2025-10016) and bypassing TCC (CVE-2025-10015). PoCs are included.
TEE.Fail attack: After RMPocalypse, BadRAM, Ahoi, Heracles, WireTap, and BatteringRAM, there's a new CPU attack that can break trusted execution environments. This one is named TEE.fail and impacts both Intel TDX and AMD SEV-SNP.
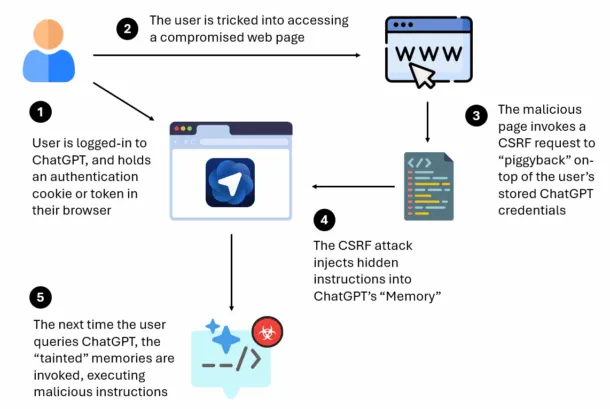
Atlas CSRF vulnerability: Attackers can use a CSRF bug to abuse an OpenAI Atlas browser's ChatGPT access credentials and inject malicious instructions into ChatGPT, per LayerX. This is also just one of the many such issues found in that browser, so I'd stay away from it for the foreseeable future.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Check First, Cloudflare, CyFirma, Gen Digital, GlobalData, Intruder, and NCC Group have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
ATT&CK v18: MITRE has released v18 of the ATT&CK framework.
New tool—readwrite: Hakan Tanriverdi and Jan Lukas Strozyk have launched readwrite, a newsletter for sharing tips on OSINT and investigative journalism.
New tool—Find-WSUS: Rob Fuller has published Find-WSUS, a tool to find hidden WSUS configurations and help guard servers against CVE-2025-59287 attacks.
New tool—Zegermans: Security researcher Michael "rootcat" has published Zegermans, a tool to generate German language passwords for password spraying attacks.
New tool—GlobalCVE: JESSE-EG-LY has launched GlobalCVE, a unified, open-source hub for global vulnerability intelligence.
New tool—Guilty-As-Yara: Security researcher Sam0rai has released Guilty-As-Yara, a Rust-based tool for testing detections for YARA rules.
BSides Dublin videos: Talks from the BSides Dublin 2025 security conference, which took place in May, are now available on YouTube.
No Hat videos: Talks from the No Hat 2025 security conference, which took place two weeks ago, are now available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq dissect a recent Chinese CERT report that the NSA had hacked China's national time-keeping service.
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about how America can better use its private sector to scale up offensive cyber activities, including espionage and disruption operations. Involving it to tackle ransomware and cryptocurrency scammers makes a lot of sense.
