Risky Bulletin Newsletter
June 25, 2025
Risky Bulletin: Hackers breach Norwegian dam, open valve at full capacity
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by Authentik. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Unidentified hackers have breached the systems of a Norwegian dam and opened its water valve at full capacity in an incident this April.
The incident took place at the Lake Risevatnet dam near the city of Svelgen in Southwest Norway.
The valve ran at full capacity for four hours before the unauthorized change was detected.
According to Norwegian energy news outlet Energiteknikk, the hack didn't put anyone in danger, barely moving water output over the dam's minimum water flow requirement.
The water went pouring 497 liters per second over the minimum, but officials say the river bed could have handled up to 20,000 liters per second.
Officials believe the hack took place because of a weak password for the valve's web-accessible control panel—which is a common problem with lots of ICS gear these days.
In all of this, it's unclear if putting the valve at full capacity was intentional or not.
This would not be the first time that random hackers breached internet-exposed panels for sensitive industrial equipment and pushed buttons or modified values at random. The 2016 Verizon DBIR report includes an example where hackers broke into an unnamed water treatment facility and modified chemical levels in what incident responders described as "random."
Malicious incidents have also happened where the modifications were intentional and targeted specific values.
Pro-Palestinian hacktivists have repeatedly hacked Israeli water treatment facilities in 2020 and attempted to modify water chlorine levels unsuccessfully.
You'd expect me to cite the Oldsmar, Florida, water utility hack from 2021, but that one has been since debunked as an accidental click by one of its employees that authorities mistook as an external hack.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Dutch DDoS attacks: Pro-Kremlin group NoName05716 is back to its old DDoS shenanigans and carried out DDoS attacks against various Dutch government websites ahead of the NATO summit set to take place in the country this week. [Additional coverage in De Telegraaf]
Saudi Games leak: A pro-Iranian hacking group named Cyber Fattah has leaked the data of athletes and visitors of the Saudi Games.
War Thunder leaks, part a bajillion: War Thunder gamers have reaffirmed their title as "best leakers on the internet" and posted a restricted operating manual for AV-8B and TAV-8B Harrier fighter jets. [Additional coverage in the UK Defence Journal]
Trezor contact form incident: A threat actor has abused the contact form of crypto-wallet provider Trezor to contact its users as part of a phishing campaign. The attackers posed as the company's tech support team and tried to lure users to phishing sites. Trezor says it has now fixed the issue.
General tech and privacy
Windows 11 restore points last 60 days now: Microsoft has modified the lifespan of Windows 11 restore points, which now last 60 days instead of 90.
Closed group add-ons allowed on AMO: Mozilla has updated its add-on store policies to allow developers to host "closed group" Firefox extensions. These are add-ons designed to be used by a private audience, such as enterprise customers.
Firefox 140: Mozilla has released Firefox 140. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest feature in this release is vertical tabs. Firefox previously supported vertical tabs, but they were a UI mess. These ones actually look like vertical tabs and also include support for pinned tabs. Pocket has also been removed from Firefox after the service shut down. Users can also "unload tabs" to free up memory.
Government, politics, and policy
EU looks to ditch Azure: The European Commission is in advanced talks with French company OVHcloud to replace Microsoft Azure as the EU's official cloud provider. According to Euractiv, the talks have been underway for several weeks and also included three other European cloud providers. Talks accelerated this month after the Trump administration imposed sanctions on four judges of the International Criminal Court. The judges had their Microsoft accounts shut down, rekindling a push for the EU's digital sovereignty.
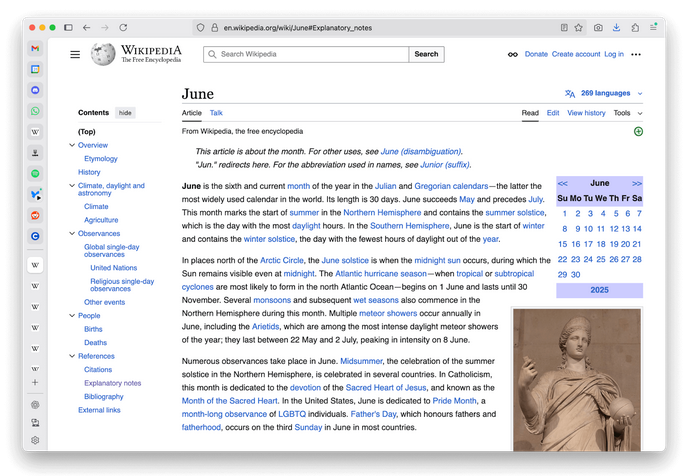
EU publishes PQC transitioning roadmap: EU member states are expected to start transitioning systems to post-quantum cryptography by the end of 2027. The transition of high-risk systems, such as critical infrastructure, should be finished by the end of 2030. States should migrate as many systems as feasible by the start of 2036. Post-quantum cryptography, or PQC, is a collection of encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers.
Russia plans a national IMEI database: The Russian government plans to create a national database of mobile device IMEI codes. IMEI codes are unique identifiers assigned to each smartphone. The Russian Ministry of Digital Affairs says the database will be used to combat financial fraud. Banning IMEI codes will allow authorities to block individual devices from mobile networks, even after fraudsters change phone numbers. [Additional coverage in Izvestia]
UK National Security Strategy 2025: Ahead of the NATO Summit in the Netherlands this week, the UK has published its National Security Strategy 2025 [PDF]. The plan promises to spend 5% of the UK GDP on national security by 2035. The plan also promises to invest some of those funds toward cybersecurity.
Frank about increasing threat, risk and vulnerability.
— Alexander Martin (@alexmartin.bsky.social) 2025-06-24T13:56:59.830Z
Common Good Cyber Fund: The Canadian and UK governments launched a fund to support cybersecurity nonprofits. The Common Good Cyber Fund will be available to nonprofits that maintain core digital infrastructure, such as DNS, internet routing, or free threat intelligence systems. It will also support organizations that provide cybersecurity assistance to high-risk individuals. The fund will be managed by the Internet Society and Global Cyber Alliance and has seed funding of $5.7 million for the next five years.
FDA urges manufacturers for more cybersecurity: The US Food and Drug Administration has urged manufacturers to prioritize cybersecurity when designing new medical products or when putting new supply chains together.
US states crack down on Bitcoin ATMs: Axios has a look at all the efforts across US states to crack down on Bitcoin ATMs and their use for scams and money laundering.
US House bans WhatsApp on Congress devices: The US House of Representatives has banned WhatsApp on member devices. The app was classified as high-risk due to the absence of on-device data encryption and the lack of transparency in how it protects user data. The House chief administrative office said Microsoft Teams, Wickr, Signal, iMessage, and FaceTime were acceptable replacements. [Additional coverage in Axios]
Iran strikes had US cyber component: The US' missile strikes on Iran's nuclear facilities included a "cyber" component, according to the Pentagon. What that was remains unknown. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
In speech about Iranian nuclear program bombing mission, the Chief of the Joint Staff indicated involvement of US cyber operators. Interesting mention - would be interested to learn more about this element! www.youtube.com/watch?v=0aCA...
— Chris Bing (@chrisbing.bsky.social) 2025-06-23T21:51:05.787Z
Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview, Fletcher Heisler, CEO of Authentik, talks to Tom Uren about the inflection points that make organizations consider rationalizing their Identity Providers (IdPs). The pair also discuss sovereign tech stacks and how to earn the trust of customers.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Four REvil members released: A Russian court has sentenced four members of the REvil ransomware to time served. The four were detained in January 2022 in a raid that arrested 14 of the ransomware group's members. They were sentenced on carding-related charges. Russian authorities previously complained US authorities shared sparse evidence of their role in ransomware attacks and then ceased all communications after its invasion of Ukraine. Four other REvil members were sentenced to jail last October on sentences from 4.5 to six years in prison. [Additional coverage in TASS/English coverage in CyberScoop]
Dark Gaboon linked to ransomware attacks in Russia: Russian security firm F6 has linked a financially motivated group named Dark Gaboon to attacks with the LockBit ransomware inside Russia. F6 tracks the group as Room155, but they are also known as Vengeful Wolf. There's a similar report like this from Positive Technologies.
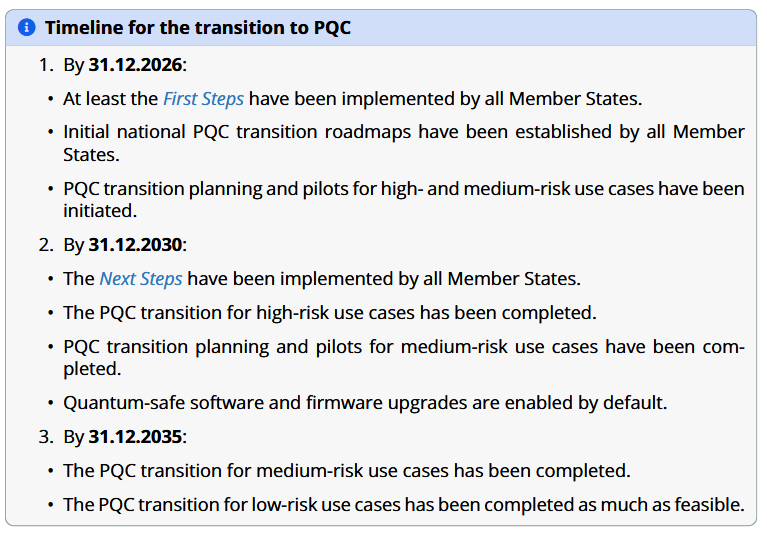
Telegram dark markets rise to fill void: Several Telegram illicit markets have risen in popularity and are filling the void left after the US sanctioned, and Telegram took down the channels of Huione Guarantee earlier this year. Congratulations to Telegram for not learning anything from its CEO's recent arrest in France and refusing to ban the new channels. </sarcasm>
After its takedowns last month, crypto tracing firm Elliptic warned Telegram that the scammers and their enablers would just shift to the next-biggest markets, and shared an extensive list of their channels and usernames with Telegram. It declined to ban any of them.
— Andy Greenberg (@agreenberg.bsky.social) 2025-06-23T17:05:31.626Z
Coinbase scammer: Blockchain sleuth ZachXBT claims to have found the identity of a major crypto-scammer named Daytwo and PawsOnHips as a New York man named Christian Nieves. The researcher says the scammer stole over $4 million worth of crypto-assets from Coinbase users by posing as Coinbase support personnel. [Additional coverage in The Shib]
Israel-Iran "cyber war": Security firms CloudSEK, Group-IB, and Trellix have published an overview of all the cyber, hacktivist, and GPS jamming activity taking place right now in the Middle East—obviously caused by the recent military conflict between Iran and Israel.
"Hacktivist activity spiked by 46% above baseline on June 13, but has since dropped by approximately 70% from its peak."
CyberAv3ngers profile: DomainTools' CTI team has published a profile on Iranian hacking group CyberAv3ngers.
Fake SonicWall app steals VPN credentials: A threat actor is distributing a malicious version of the SonicWall SSL VPN NetExtender app that steals VPN credentials from infected users.
ConnectWise abused to sign malware: Since March, a threat actor has abused the ConnectWise installer to sign malware. The EvilConwi group exploited attributes in the installer that were exempted from the certificate signing to load and run their malware from the installer itself. German security firm GDATA spotted and reported the abuse to ConnectWise on June 12. The company rotated its signing certificate a day later.
Malware technical reports
WordPress Core malware framework: Wordfence has spotted a new modular malware framework designed for credit card skimming and WordPress credential theft. The malware is typically installed on hacked WordPress sites as a plugin named WordPress Core.
Pulsar RAT: ThreatMon has published an analysis of the Pulsar RAT, a .NET RAT considered a continuation of the older Quasar RAT.
SparkKitty: Kaspersky has spotted a new version of the SparkCat malware, which they named SparkKitty. This is a mobile trojan that infected both Android and iOS and was using OCR to scan the victim's images for crypto-wallet seed phrases.
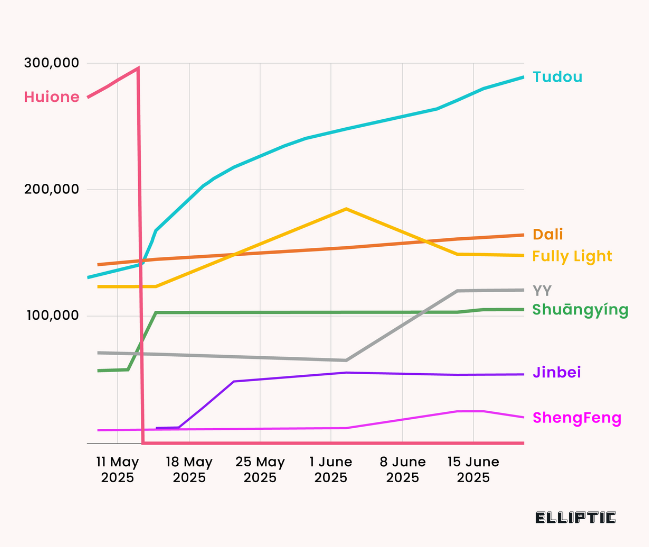
LapDogs botnet: SecurityScorecard has discovered a new botnet used by Chinese hackers to hide their attacks. Named LapDogs, the botnet runs on top of a custom backdoor named ShortLeash. The botnet has infected more than 1,000 devices, with most being SOHO routers. At least one Chinese APT group named UAT-5918 used the botnet to hide its operations.
Sponsor section
Authentik is an open-source identity provider that is also offered with paid enterprise features. In this demo, CEO Fletcher Heisler and CTO Jens Langhammer walk Risky Business host Patrick Gray through an overview and a demo of the technology.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
TAG-140's DRAT v2: Recorded Future has published a report on the new version of DRAT, a remote access trojan used by TAG-140 (SideCopy), a suspected Pakistani APT.
"The deployment of DRAT V2 reflects TAG-140's ongoing refinement of its remote access tooling, transitioning from a .NET-based version of DRAT to a new Delphi-compiled variant. Both versions are among numerous RATs the group has leveraged, such as CurlBack, SparkRAT, AresRAT, Xeno RAT, AllaKore, and ReverseRAT, indicating a pattern of rotating malware use."
APT36 (Transparent Tribe): Indian security firm CyFirma has spotted a new APT36 campaign targeting the Indian defense sector. APT36 is a suspected Pakistani APT.
APT-Q-14: Chinese security firm QiAnXin says a cyber-espionage group tracked as APT-Q-14 is using a zero-day XSS vulnerability in an unnamed webmail platform to target domestic organizations. The group also used Microsoft's ClickOnce deployment technology to install their malware. QiAnXin says the group is part of the larger DarkHotel group, previously linked to South Korea by other security firms.
APT-C-06: Qihoo 360, another Chinese security firm, also published a report on DarkHotel, which they call APT-C-06, but this one looks at a campaign targeting North Korean trade personnel.
UAC-0001 (APT28): CERT-UA has published a report on a UAC-0001 campaign that targeted Ukrainian government agencies with the BEARDSHELL and COVENANT malware.
Havoc analysis: Fortinet has published an analysis of a Havoc C2 framework sample that was used in a Middle East APT intrusion at a critical infrastructure organization.
PwC on APT attribution: PwC's security team has published a detailed write-up on their process of attributing threat actors.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Libxml2 makes security reports public: The lead developer of the Libxml2 library has announced that all vulnerability reports submitted to the project will be public by default. Nick Wellnhofer says security flaws will also no longer have a deadline to release a fix, and they'll be patched when he has time. Wellnhofer hopes the new policy will make downstream users nervous and encourage them to contribute back to the project. The Libxml2 library is currently used in macOS, Windows, and Linux operating systems.
Yealink vulnerabilities: CloudAware researchers have disclosed several vulnerabilities in the Yealink VoIP phone system. Yealink acknowledged the issues and asked customers to upgrade to newer versions.
WinRAR RCE: RARLAB has released a security update for the WinRAR file-archiving software to patch a vulnerability that can be abused for remote attacks. Tracked as CVE-2025-6218, the vulnerability is a path traversal bug that can allow attackers to run code on a user's system. The issue only impacts WinRAR Windows versions.
Splunk security updates: Cisco has released four security advisories for its Splunk SIEM platform.
Echo Chamber Attack: NeuralTrust has published details on Echo Chamber, a new LLM jailbreaking technique.
"Unlike traditional jailbreaks that rely on adversarial phrasing or character obfuscation, Echo Chamber weaponizes indirect references, semantic steering, and multi-step inference. The result is a subtle yet powerful manipulation of the model's internal state, gradually leading it to produce policy-violating responses."
New SSRF technique: Assetnote, now with Searchlight Cyber, has developed a new SSRF technique that uses HTTP redirect loops to leak the full content of HTTP responses.
Phantom Persistence technique: Grant Smith, the President of the Phantom Security Group, has posted details about Phantom Persistence, a new Windows persistence technique.
"It was a bit disappointing to hear that my submission for a short talk on this technique was declined by DEF CON but that's good news for you all. You get this technique a few weeks ahead of schedule!"
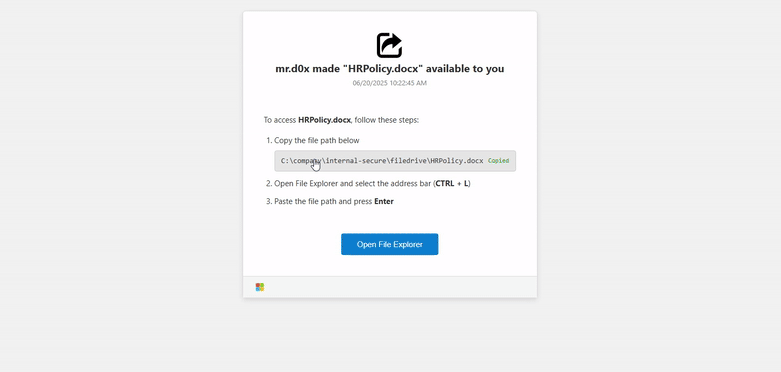
FileFix technique: Security researcher mrd0x has developed an alternative to the ClickFix technique named FileFix. The technique works by tricking users into copying and pasting a file path into Windows Explorer. The trick is that an attacker can modify the copied file path to prepend PowerShell commands before it and add a bunch of space characters to hide them from view.
Infosec industry
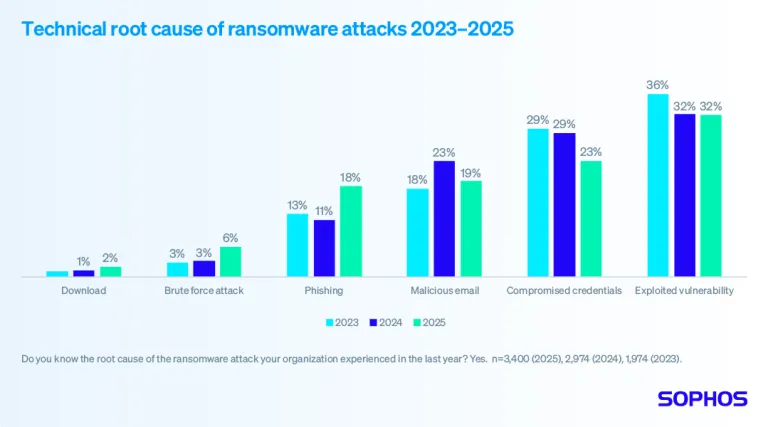
Threat/trend reports: AM Best, Cobalt, Incogni, Sophos, and WithSecure have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats. From the AM Best report:
"Premiums generated from cyber insurance coverage declined by 2.3% to slightly less than $7.1 billion in 2024 compared with a year earlier, marking the first ever decrease in the segment since the data was first collected in 2015."
CIDP shuts down: Cybersecurity firms have shut down a project that offered free security services to critical infrastructure organizations. The Critical Infrastructure Defense Project was established in 2022 by Cloudflare, CrowdStrike, and Ping Identity. The program was set up after Russia's invasion of Ukraine to help US organizations defend against possible Russian cyberattacks and sabotage. Its main beneficiaries were hospitals, water systems, and power utilities. [Additional coverage in NextGov]
New tool—XMRogue: Security firm Akamai has developed a new tool named XMRogue that can be used to sabotage crypto-mining botnets. The tool works by joining the botnet and submitting bad computations to Monero mining pools. Repeated submissions will get the botnet banned from the mining pool and crash the attacker's earnings. The technique works best against crypto-mining botnets that use proxies to submit computations from their infected systems.
New tool—haveibeenpwned.watch: Snap security engineer George-Andrei Iosif has released haveibeenpwned.watch, a portal that displays the data from the haveibeenpwned.com database in easy-to-understand graphs.
CODE BLUE 2024 videos: Talks from the CODE BLUE 2024 security conference, which took place last November, are available on YouTube.
SANS CTI Summit 2025 videos: Videos from the SANS Cyber Threat Intelligence Summit 2025 security conference, which took place at the end of January, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq dive into the motivations and actions of Predatory Sparrow, a purported hacktivist group that has been attacking Iran for the last five years and has leaped into the Iran-Israel work.
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about a Minnesota man who used people-search services to locate, stalk, and eventually murder political targets. They also discuss the purported hacktivist group Predatory Sparrow weighing in on the Iran-Israel conflict.
