Risky Bulletin Newsletter
February 11, 2026
Risky Bulletin: Chinese cyber-spies breached all of Singapore's telcos
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by Trail of Bits. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Singapore's cybersecurity agency says that a Chinese cyber-espionage group has breached all of the country's four major telecom providers—M1, SIMBA Telecom, Singtel, and StarHub.
The Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA) attributed the attacks to a group tracked as UNC3886.
The breaches took place last year and the agency spent 11 months with industry groups investigating and evicting the hackers from the compromised networks.
The intruders allegedly stole a "small amount of technical data" to aid future intrusions but investigators didn't find evidence they stole customer details.
The attacks allegedly involved zero-days in the telcos' firewalls and rootkits to maintain persistence.
According to technical reports from Google, Sygnia, and Trend Micro, the group has a long history of using exploits in networking and enterprise gear, such as Fortinet, Juniper, Ivanti SecureConnect, and VMware ESXi and vCenter.
The group is widely considered one of the most prolific Chinese espionage groups over the past two-three years, together with the more famous Salt Typhoon, another Chinese APT group specialized in telco hacks.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Hacktivist scrapes stalkerware provider: A hacktivist has scraped and leaked more than 536,000 records from a Ukrainian company that sells stalkerware products. The data includes email addresses and partial payment information for individuals who bought spyware and phone-tracking services. The data covers purchases of tools like Geofinder, uMobix, and Peekviewer, formerly known as Glassagram. All three are products developed by a Ukrainian company named Struktura. The hacktivist, named wikkid, has published the data on a known hacking forum. [TechCrunch]
Substack breach impacted 663k: Around 663,000 Substack users had their personal data exposed in a security breach. The incident appears to be a scrape of public Substack data, matched to email addresses.
Nova Scotia Power cyberattack: Seems that the sequel trend from Hollywood is spreading. Canadian regulators are planning a two-part investigation of a cyberattack that crippled Nova Scotia Power last year. The first investigation will look at the technical aspects of the breach. The second will look at how the company stored customer data and how it estimated bills after the incident. Customers complained about higher bills after the incident. More than 280,000 customer records were stolen in the hack. [North Shore News]
General tech and privacy
Discord to implement global age verification: Discord is rolling out age verification checks for all users worldwide starting next month. All users will be required to verify their age to access Discord content, either by taking a video selfie or uploading a government ID. All Discord users will receive a "teen-appropriate" experience on the platform until they verify their age. The news was met with huge user backlash since the platform exposed documents related to age verification checks in a security breach last October.
While this absolutely sucks, we are going to see a lot more places implementing universal global age verification over this next year, because the number of states and countries legally requiring it has gotten to the point no one can keep up anymore.
— rahaeli (@rahaeli.bsky.social) 2026-02-10T10:42:36.861Z
Microsoft announces two new security features: Microsoft will roll out two new security features in Windows 11 in the coming months. The new Windows Baseline Security Mode will enable runtime integrity safeguards enabled by default to prevent tampering or unauthorized changes. The new Windows User Transparency and Consent will add a smartphone-like permission system that prompts users when apps access sensitive resources or perform hidden installs.
Intel releases TDX 1.5: Intel has released version 1.5 of Trust Domain Extensions (TDX), a technology that allows Intel CPUs to run confidential computing tasks. The new version introduces two new features named Live Migration and Trust Domain Partitioning. Google's security team has audited the code before release, finding one major vulnerability that could have allowed the full compromise of TDX execution environments.
Waymo cars use human assistance: Self-driving car company Waymo uses remote operators to assist cars in problematic driving scenarios. The operators are based in the US and the Philippines, Waymo Chief Safety Officer Dr. Mauricio Peña told senators in a Senate hearing last week. The remote staff don't take remote control of the car, but provide guidance to the Waymo software on how to proceed. [People]
France's GDPR enforcement: France's data protection agency handed out 83 GDPR fines last year, totalling more than $486 million.
FTC warns 13 data brokers: The US FTC has sent warning letters to 13 data brokers who sold the data of American citizens to foreign adversaries. The companies have allegedly failed to follow the US Protecting Americans' Data from Foreign Adversaries Act of 2024. The law forbids data brokers from selling sensitive data to countries such as China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea.
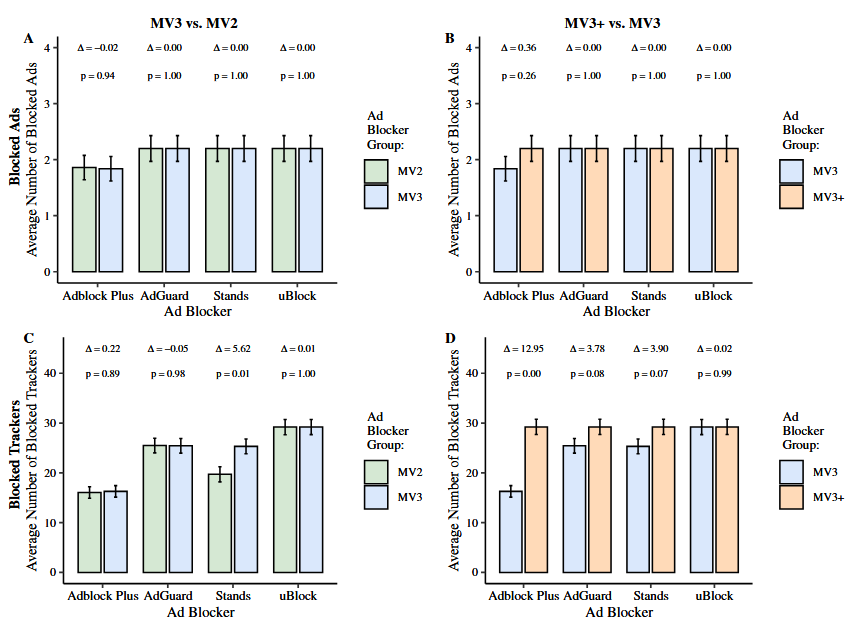
Chrome MV3 not bad after all: Ad blocker vendors appear to have adapted to Chrome's new extensions API, also known as Manifest V3. An academic study by the Goethe University in Frankfurt found no statistically significant reduction in ad-blocking effectiveness compared to the old Manifest V2. Researchers also didn't find a noticeable difference between ad blocking efficiency on Chrome compared to Firefox. The study looked at four popular ad blockers—AdBlock Plus, AdGuard, Stands, and uBlock.
Government, politics, and policy
Russia restricts Telegram again: Russia's internet watchdog has restricted access to the Telegram instant messaging service. Russian officials said the app has failed to crack down on fraud and terrorist activities. This is the third time that Russia blocks access to Telegram after August and October last year. The Russian government launched its own instant messaging app named MAX last June. [RBC // The Kyiv Independent]
Russia to create one big financial database: The Central Bank of Russia will build a central database to hold the financial information of every citizen. The database will hold information on how many cards each citizen owns and at what banks. Russians won't be allowed to own more than 20 cards and no more than five at the same bank. The new system is set to go live within the next year. [RBC]
India's Aadhaar adds offline verification: The Indian government has launched a new mobile app that can perform offline verification for a user's identity or age against the country's Aadhaar biometrics database. The app will allow users to prove they're above a certain age without sharing their date of birth. Indian officials will use the app for primarily policing and the hospitality sector. [TechCrunch]
Nigeria to publish a cybersecurity framework: The Nigerian government is working on a national cybersecurity framework. The new framework is expected to go live later this year and will require companies to meet minimum cybersecurity requirements. It will also introduce breach-reporting timelines, protocols for sharing threat intelligence, and a coordinated response plan for major cyber incidents. [Bloomberg]
US Air Force bans smart glasses: The US Air Force has banned service members from wearing smart glasses while in uniform. The new rule comes after reports that Meta smart glasses are being used to secretly record individuals without their knowledge or permission. The glasses could be used to record classified or sensitive material.
FISA renewal talks: The White House will hold meetings with top Republican lawmakers on how to renew FISA Section 702 surveillance powers, set to expire in April. [The Record]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Tom Uren talks to Trail of Bits CEO Dan Guido about how Trail of Bits is reworking its business processes to take advantage of AI. Dan talks about what it takes to make AI agents reliable and trustworthy and how that will give the company an edge by making its work both better and faster.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Morele hacker arrested after eight years: Polish authorities have arrested a 29-year-old for hacking a popular Polish online electronics marketplace. The suspect was detained eight years after he breached the Morele.net portal. The man has admitted to the hack and then leaking the personal details of more than two million users. He also attempted to scam Morele customers. [TVP World]
JokerOTP dev arrested in the Netherlands: Dutch police have detained a 21-year-old from the city of Dordrecht on cybercrime charges. The suspect allegedly sold a phishing kit on Telegram that could intercept one-time passwords. Named JokerOTP, the kit could call victims and ask for the OTP code they just received when an attacker was trying to access accounts with valid credentials.
Russia grants political asylum to Spanish professor: Russian authorities have granted political asylum to a Spanish national with connections to the NoName057 hacktivist group. Enrique Arias Gil was placed on the EU's most wanted list in September. He allegedly ran a Telegram channel named Russian Disinformer where he promoted NoName's DDoS attacks to Spanish-speaking audiences. Gil has also filed paperwork to become a Russian citizen. [TASS]
Crypto scammer sentenced to 20 years: A US judge has sentenced a Chinese national in absentia to 20 years in prison for laundering funds from Cambodian cyber scam compounds. Daren Li was part of a larger group that laundered more than $73 million through a web of shell companies and international bank accounts. Li was arrested in May 2024 as the US started cracking down on an emerging cybercrime trend known as "pig butchering." He received the maximum sentence for his crimes after he cut off his ankle monitor and fled the US in December.
US charges FanDuel fraudsters: The US has charged two men with using stolen identities to sign up for new FanDuel accounts. Amitok Kapoor and Siddharth Lillaney created the accounts to receive free credits and bonus bets. US officials say the two used the stolen identities of more than 3,000 people to defraud FanDuel of more than $3 million in gambling earnings over the past five years.
EmEditor group still active: Stormshield has discovered new infrastructure linked to the group behind the compromise of the EmEditor website. The report concludes that the attacker continued its activity even after being exposed by QiAnXin and Trend Micro.
Has anyone looked if the Notepad++ and EmEditor incidents are related in any way?
— Catalin Cimpanu (@campuscodi.risky.biz) 2026-02-10T12:36:32.453Z
0APT group is fake: Guidepoint Security says a new ransomware group that appeared at the end of January and named 0APT is a fraud, using a dark web leak site with fabricated victim names or with real names for companies that didn't suffer any security incidents. DataBreach.com reached the same conclusion last week.
IABs target Ivanti servers: Threat actors specialized in initial access are exploiting Ivanti EPMM servers using two recent zero-days. According to security firm Defused, a coordinated hacking campaign started on February 4. Attackers are deploying an in-memory Java loader. Customers who purchase access to the hacked device use this loader to deploy their own malware.
Threat actors targeting the Defense Industrial Base: Google Cloud has published a report looking at all the threat actors targeting companies in the Defense Industrial Base. The report goes over the main groups from all major foreign adversaries and what their main focus has been over the past decade.
The malicious ads ecosystem: According to Juniper Research, online tech platforms made £3.8 billion ($5.2 billion) in revenue from malicious or scam ads in Europe alone, which shows exactly why most of these sites rarely follow through on abuse reports to disable ads and offending accounts.
Telegram QR code auth hijacks: Threat actors are tricking users into scanning malicious QR codes designed to authenticate an attacker's device against their Telegram account, effectively giving them access to past messages and the account.
Hacktivism evolves into hybrid warfare: An Orange Cyberdefense report concludes that hacktivism has evolved from a form of digital protest into the realm of hybrid warfare.
Malware technical reports
Global Group ransomware: Forcepoint researchers have spotted malspam campaigns originating from the Phorpiex botnet that are delivering the Global Group ransomware strain.
Reynolds ransomware: There's a new ransomware strain in town named Reynolds. Only one victim has been listed on its dark web leak site so far.
Babuk 2.0 was a fake: Researchers at Picus Security conclude that the Babuk 2.0 ransomware that was active last year was not related to the first iteration of the operation (circa 2021), and was merely a rebranded version of the LockBit ransomware abusing Babuk's name.
More VoidLink: Ontinue has published its own insight on the new VoidLink AI-generated Linux malware, first documented by Check Point last month.
GuLoader: Zscaler researchers look at the anti-analysis techniques used by the GuLoader malware, also known as CloudEye.
SSHStalker botnet: There's a new IRC botnet in town named SSHStalker. The botnet uses an automated mass-scanning and infection system to target smart devices running very old Linux kernels.
SHub Stealer: A threat actor is posing as legitimate software developers and publishing malicious GitHub repos that deploy infostealers on Windows and macOS. One of the infostealers is a new macOS threat named SHub Stealer.
LTX Stealer: CyFirma has identified a new infostealer named LTX Stealer that is being used to target Windows systems. LTX embeds and runs from a full Node.js runtime.
ZeroDayRAT: iVerify has spotted a new mobile spyware named ZeroDayRAT that can target both Android and iOS and is currently being sold on Telegram.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Casey Ellis chats with Keith Hoodlet from Trail of Bits. Keith is Trail of Bits’ director of engineering for AI, machine learning and application security and he joined Casey to talk about why prompt injection attack techniques that target AI are an unsolvable problem.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Poland grid attack: Midnight Blue looks at the ABB vulnerability used by Russian hackers in their attack against Poland's energy grid and how it could have been used to brick OT gear in the targeted network.
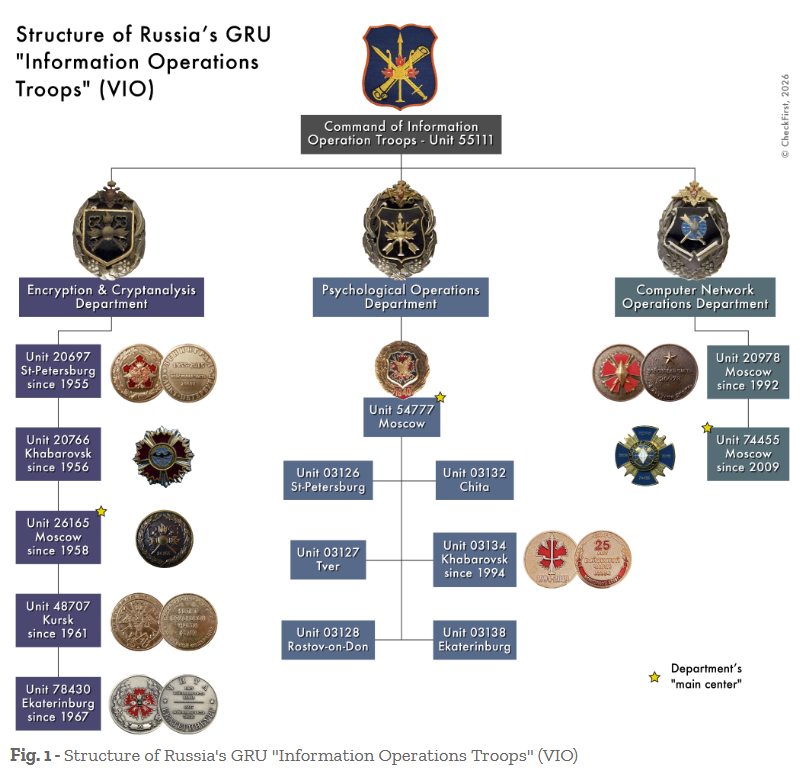
Medals expose Russia's info-ops troops: Security researchers have uncovered the internal structure of Russia's information operations troops by analyzing 118 photographs of insignia, patches, and military pennants. The secretive Information Operations Troops (VIO) operate under Russia's military intelligence service, known as the GRU. They were established in 2014 by the Russian government in response to the Snowden revelations. Finnish security firm CheckFirst was able to track down VIO units, its chain of command, and identified their facilities across Russia. CheckFirst also tracked down the FSB's SIGINT units based on their medals in similar research last year.
Transparent Tribe (APT36): Aryaka looks at the recent surge in activity from Pakistani APT group Transparent Tribe (APT36), a surge driven by the recent military conflict between India and Pakistan last year. The report analyzes three RATs recently used by the group in attacks, namely Geta, Ares, and Desk RAT.
UNC1069 profile: Google Mandiant has published a profile of UNC1069, a North Korean financially motivated threat actor that's been around since 2018 and has been recently focusing on the cryptocurrency scene.
"This investigation revealed a tailored intrusion resulting in the deployment of seven unique malware families, including a new set of tooling designed to capture host and victim data: SILENCELIFT, DEEPBREATH and CHROMEPUSH. The intrusion relied on a social engineering scheme involving a compromised Telegram account, a fake Zoom meeting, a ClickFix infection vector, and reported usage of AI-generated video to deceive the victim."
CyberPeace leak: A report looks at documents that leaked from a Chinese company called CyberPeace that develops a training platform to rehearse cyberattacks against the critical infrastructure. [The Record]
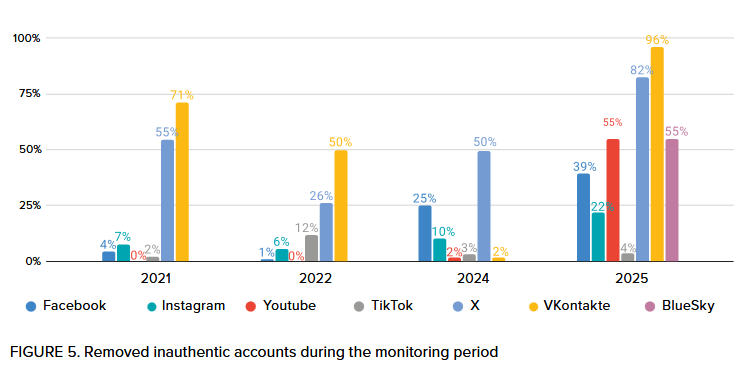
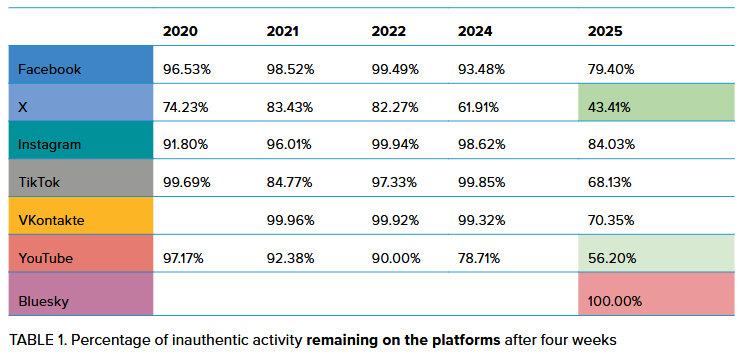
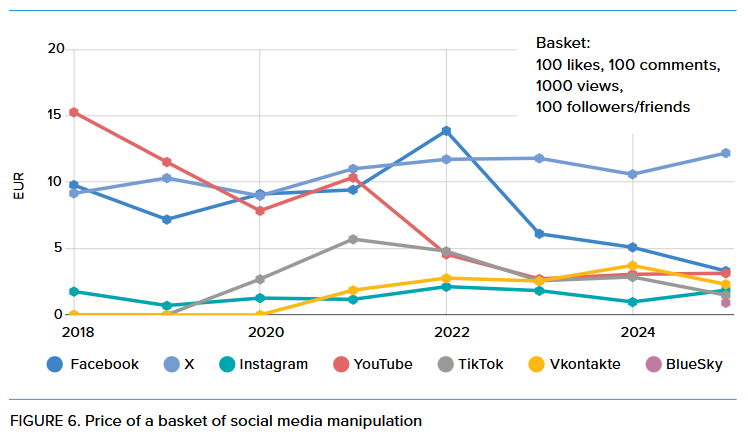
NATO tests social media platforms: Social media platforms are getting better at spotting and removing coordinated influence operations. A NATO study of seven platforms found that disinformation and spam are cheap to buy using just a few dollars. While platforms deactivated more test accounts than in previous years, the numbers are still very low and most of the disinformation remains online. VKontakte and Twitter/X removed the most accounts, while BlueSky failed to remove any of their inauthentic behavior. [h/t Lukasz Olejnik]
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was the February 2026 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates from Adobe, Microsoft, IBM, SAP, Fortinet, Cisco, Ivanti, Intel, AMD, Supermicro, Schneider Electric, Siemens, Synology, Rapid7, BeyondTrust, and Kubernetes. Other projects and companies like ASUS, D-Link, Zyxel, HPE, Dell, Moxa, Samsung, Qualcomm, Splunk, ESET, Drupal, Django, Roundcube, and GitLab released security updates earlier this month.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday: This month, Microsoft patched 58 vulnerabilities, including six actively exploited zero-days.
- CVE-2026-21510: a Windows SmartScreen and Windows Shell security prompts bypass
- CVE-2026-21514: a Word vulnerability that allows an attacker to bypass OLE mitigations
- CVE-2026-21513: an Internet Explorer bug to bypass security controls and potentially execute code via malicious HTML or LNK files
- CVE-2026-21519: a Windows Desktop Window Manager elevation of privilege vulnerability
- CVE-2026-21533: a Windows Remote Desktop Services elevation of privilege vulnerability
- CVE-2026-21525: a Windows Remote Access Connection Manager denial of service bug
You say "Security Feature Bypass"... I say.... "Remote Code Execution": msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide...
— tlansec (@tlansec.bsky.social) 2026-02-03T12:14:45.244Z
Unpatched Intego bugs: Quarkslab says Intego has failed to patch several vulnerabilities in its macOS security products despite ample time to do so.
W3 Total Cache PoC: RCE Security has published a proof-of-concept for an October patch for an unauthenticated command injection vulnerability in the W3 Total Cache WordPress plugin, also tracked as CVE-2025-9501. The plugin is one of the most popular in the WordPress ecosystem.
New VPN deanonimization vector: VPN users can be deanonimized based on the ad-block filter lists installed in their browser. Users can be traced back to specific countries based on domains included in country-specific ad-blocker lists. According to Melvin Lammerts, the technique is limited to the availability of such lists and if users use ad-blockers in the first place.
GRP-Obliteration attack: Microsoft has discovered that a technique normally used to fine-tune LLMs after their deployment can be used to remove its safety features. The company calls the attack GRP-Obliteration after the technique's name—Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Microsoft says tests were able to unalign safety features across 15 of today's most used LLMs, from DeepSeek to GPT and Llama.
Claude DXT RCE: LayerX researchers have discovered a remote code execution vulnerability in the Claude Desktop Extensions (DXT) app.
"A single Google Calendar event can silently compromise a system running Claude Desktop Extensions. The flaw impacts more than 10,000 active users and 50 DXT extensions."
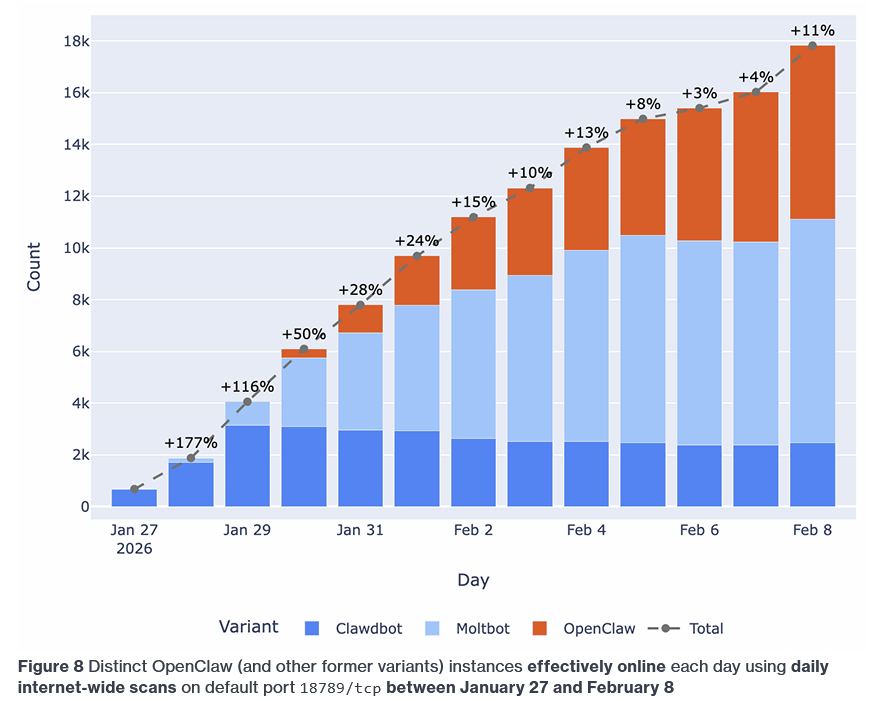
OpenClaw exposure grows: The number of internet-exposed OpenClaw instances has grown from 1,000 to 30,000 instances in just ten days, according to new research from BitSight. SecurityScorecard has that number even higher, at 135,000. I just can't take this technology seriously. Sorry!
"What our data shows is that OpenClaw is being deployed fast, at scale, and often exposed to the public internet. More importantly, we’re already seeing it show up in sensitive industry sectors."
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Check Point, CNIL, Intel471, Juniper Research, Orange Cyberdefense, Picus Security, Tines, and TIOBE have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
EU approves Google's Wiz deal: The European Commission has approved Google's $32 billion acquisition of Israeli cloud security startup Wiz.
New tool—Quantickle: The RSA Conference has released Quantickle, a browser-based network graph visualization tool to help visualize and analyze connected data of any type, specifically faceted towards threat intelligence.
New tool—Http11Probe: Software engineer Diogo Martins has released Http11Probe, a compliance and security testing suite for HTTP/1.1 servers.
BSides Munich videos: Talks from the BSides Munich 2025 security conference, which took place last November, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about why the world is destined to be perpetually insecure.
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about Google's cyber disruption unit taking aim at the IPIDEA residential proxy network. The network was a cybercrime enabler that was used by hundreds of threat actors for crime and espionage.
