Risky Bulletin Newsletter
May 23, 2025
Risky Bulletin: Authorities and security firms take down DanaBot and Lumma Stealer
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by SpecterOps, the experts in Attack Path Management. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
A coalition of law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity firms have dealt two major blows to the cybercrime ecosystem this week by taking down a prodigious malware botnet named DanaBot and Lumma Stealer (aka LummaC2), today's most popular and widely used infostealer platform.
The Lumma Stealer takedown
The takedowns took place on separate days and were unrelated to each other. The first took place on Wednesday and targeted Lumma, a type of malware that infects Windows systems, extracts login credentials from various apps, and sends them to an attacker's servers.
Over 2,300 domains that hosted Lumma Stealer control panels and payloads now show a law enforcement seizure banner and are sinkholing traffic from infected victims.
According to Microsoft, these domains had received pings from more than 394,000 Windows computers, which were most likely infected with the Lumma malware in the past.
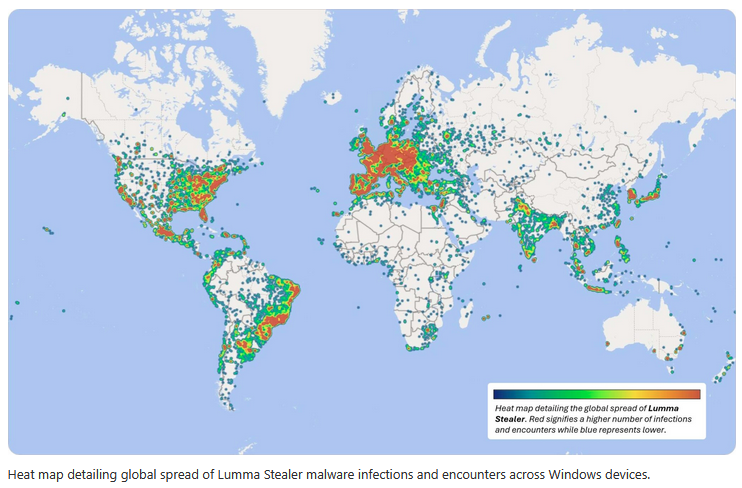
Slovak security firm ESET says it tracked 3,353 unique Lumma Stealer C&C domains since June of last year, which basically means the takedown crushed quite a considerable portion of the Lumma Stealer backend infrastructure.
Currently, there are hundreds of different infostealer strains that are marketed on Telegram, the dark web, and various underground hacking forums.
What made Lumma a success above the rest was its business model, which was more operationalized and organized than what rivals were offering.
For a few bucks, you would get the Lumma malware itself, but also your personalized control panel where victims would send their data. Customers who bought Lumma also had the option to take all the credentials they collected and sell them on a private marketplace operated by the Lumma creators themselves.
This made threat actors flock to Lumma ever since it was released in February 2023 and allowed it to effectively monopolize the infostealer market.
Lumma had a simple point-and-click process that even the dumbest of threat actors could handle and a marketplace where they could monetize their stolen caches.
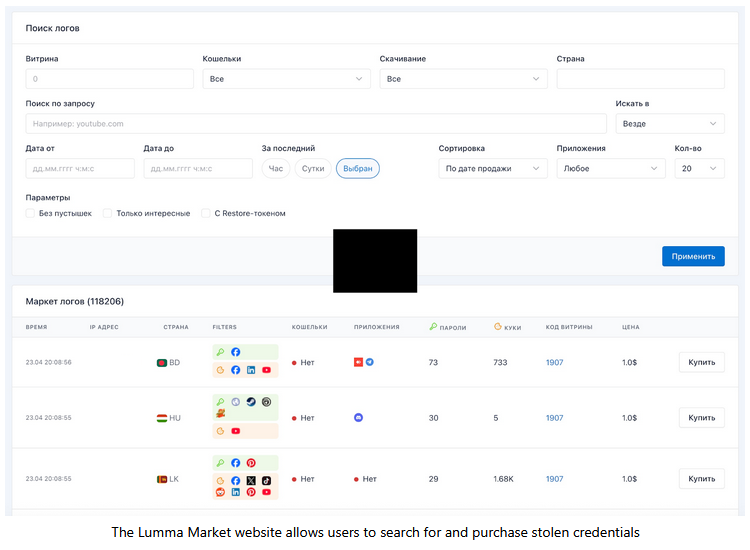
Europol says it seized the marketplace domain, too, which means Lumma customers don't have a place to sell their stolen credentials anymore.
Authorities didn't specify if they seized servers and backend databases, but according to a message the FBI allegedly posted in Lumma's private Telegram channel, the Bureau does appear to have the servers and data on Lumma customer data as well.

While some parts of Lumma Stealer infrastructure are still live, I'd wager the entire operation is most likely done and dusted.
The infostealer market is flooded and the competition is beyond fierce. Lumma lost the trust of its users, and by the time Lumma admins return online, their customers will have already moved shop somewhere else. If I'm a cyber crook, I'm certainly not hanging around a service that has the FBI and Europol defacing its domains and trolling their Telegram.
Press releases associated with the Lumma takedowns: Europol, US Department of Justice, CISA, Microsoft, Microsoft (again), ESET, Bitsight, Cloudflare, CleanDNS.
DanaBot takedown
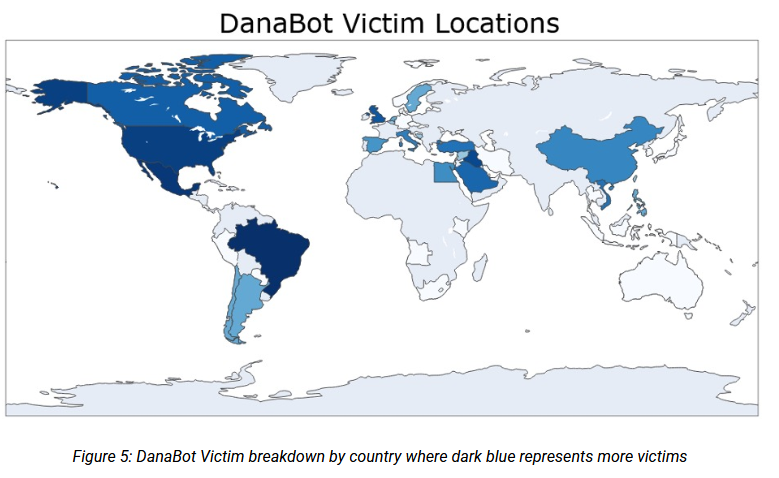
Unrelated to the first, a similar coalition of law enforcement and cybersecurity firms also took down DanaBot, a malware botnet that infected Windows systems and then sold access to them to other cybercrime operations, such as cryptominers, carders, or ransomware groups.
Ever since it launched in 2018, the botnet has infected over 300,000 systems and has been identified as the initial entry access point for several ransomware attacks.
It was never a big botnet, but it grew in popularity after a similar law enforcement effort called Operation Endgame took down six of its rivals last May (Bumblebee, IcedID, Pikabot, Smokeloader, SystemBC, Trickbot)
Its takedown is now being referred to as Operation Endgame II.
Besides seizing server and domain infrastructure, US authorities have also unsealed charges against 16 DanaBot members, including the two leaders, Aleksandr "JimmBee" Stepanov and Artem "Onix" Kalinkin, both from Novosibirsk, Russia.
One thing noted by security researchers about DanaBot was that from a simple malware loader, the malware had slowly evolved into a full-blow infostealer, too, showing a general trend in the cybercrime ecosystem for malware that can collect stolen creds and how central they are for enabling the broader array of cybercrime intrusions.
Press releases associated with the DanaBot takedowns: US Department of Justice, Lumen, Team Cymru, ESET, Proofpoint, Zscaler, Intel471.
Risky Business Podcasts
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
TeleMessage data starts revealing its secrets: An early analysis of the stolen TeleMessage data has found conversations from more than 60 US government users. Reuters obtained copies of the TeleMessage data after hackers provided the stolen files to the DDoSecrets project. The files didn't contain the conversations per-se, but metadata about who was exchanging messages. Reuters linked some of the metadata to US diplomatic staffers, customs officials, disaster responders, and at least one White House staffer and Secret Service agent.
Marks & Spencer expects record losses: UK retail chain Marks & Spencer expects to incur over £300 million (~$402 million) from a recent cyberattack that has crippled its internal network. The sum represents lost profit from lost online orders and recovery costs. Insurance companies Allianz and Beazley are expected to cover up to £100 million related to recovery costs. The company says the disruption is expected to continue through July. [Additional coverage in The Telegraph]
M&S point of entry: The point of entry for the M&S hack listed above has also been identified as a social engineering attack against an employee at a third-party contractor Tata Consulting Services. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
Infostealer DB leaks online: Security researcher Jeremiah Fowler has discovered a publicly exposed database that contained over 184 million pairs of login credentials. Fowler believes the database most likely stored login credentials collected by an infostealer operation. The hosting provider shut down the DB after being contacted by journalists.
Coinbase hack update: Coinbase says its recent breach impacted around 70,000 customers only and started back on December 26, last year.
Opexus hack impacts US government networks: Two rogue employees from IT company Opexus have stolen data and destroyed over 30 US government databases. The incident impacted the US Internal Revenue Service and the General Services Administration. Bloomberg identified the two employees as brothers Suhaib and Muneeb Akhter. The two previously served prison sentences for hacking the State Department in 2015. [Additional coverage in the Insurance Journal]
Discord dump: A team of Brazilian researchers scraped over 3,000 Discord servers and published over two billion messages online. [Additional coverage in 404 Media]
Cetus Protocol crypto-heist: Hackers have stolen $223 million worth of crypto tokens from the Cetus decentralized exchange. The attackers exploited vulnerabilities in several smart contracts that managed the platform's asset liquidity pools. Cetus says it worked with industry partners and has already frozen $162 million of the stolen assets.
General tech and privacy
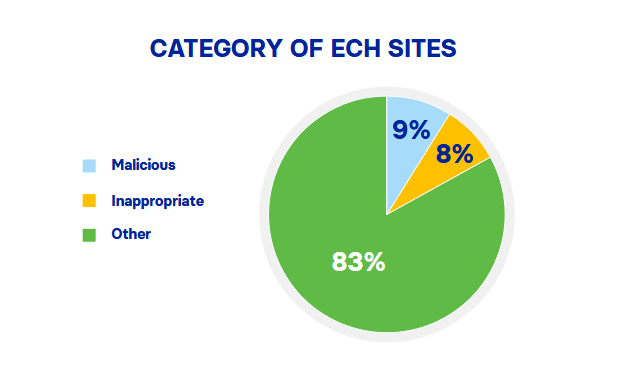
ECH adoption remains low: A Corrata report found that less than 0.01% of TLS connections used the ECH protocol and that ~17% of these ECH-enabled sites were considered suspicious.
PQC in Red Hat: Something I missed from September is that Red Hat is also adding PQC (post-quantum cryptography) support in its products, too. Microsoft announced support for this earlier this week.
6 GHz band exhaustion: A CableLabs study warns that the current 6 GHz unlicensed spectrum is close to exhaustion due to ever-increasing use.
Sovereign Google Cloud: Because anti-US sentiment is rising across Europe due to Trump's long list of anti-EU and pro-Kremlin actions, Google Cloud put out a blog post to reassure European governments that their local EU cloud systems are "sovereign" and safe from US spying. Talks about an EU cloud provider have been intensifying as of late, with Germany, France, and the Netherlands leading the charge.
Signal blocks Recall screenshots: Signal has added a new security feature named Screen Security that will block Windows Recall from taking screenshots of the Signal app window.
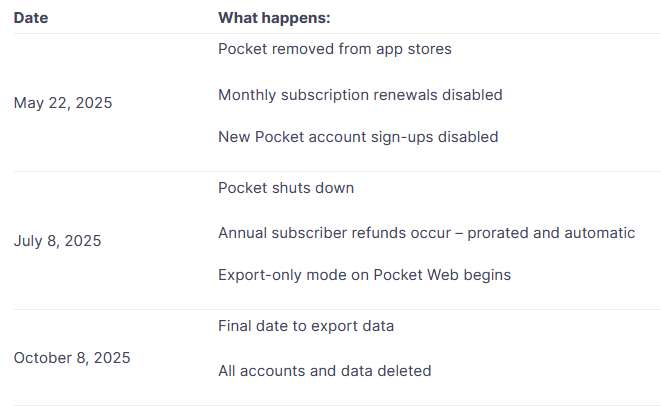
Mozilla to shut down Pocket: Mozilla will shut down its read-it-later URL saving service Pocket on July 8.
Government, politics, and policy
US Senator goes after Spotify: US Senator Maggie Hassan has sent a letter [PDF] to Spotify asking the platform to explain how it plans to crack down on fake podcasts hosted on its platform that act as ads and promote various drugs. The letter comes after Business Insider found over 200 fake podcasts on the platform earlier this month. Most podcasts were a few seconds long and spelled out domains where users could buy drugs.
PCLOB firings deemed illegal: A judge has ruled that the White House firing two Democrats from the Privacy and Civil Liberties Oversight Board (PCLOB) was illegal. [Additional coverage in The Record]
ODNI wants a centralized data broker platform: The US government is looking for a company to build a centralized marketplace where smaller government agencies can buy commercially available information from data brokers. Named the Intelligence Community Data Consortium, the portal will aggregate data from different data brokers and use AI to process and deduplicate the data. The portal has been ordered by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence and will be made available to at least 18 different US government agencies and their offices. [Additional coverage in The Intercept]
Sen. Wyden calls out telco failures: US Senator Ron Wyden (D-OR) has called out US telcos for their failure to notify government officials whenever their communications were tapped by law enforcement.
Russia to track foreigners with mandatory app: The Russian government has passed a law that would require any foreigner visiting Moscow to install a tracking app on their smartphone. The new rule enters into effect at the start of September and will run for a four-year trial period. Foreign diplomats, minors, and Belarusian citizens are exempt. [Additional coverage in Novaya Gazeta]
Tanzania blocks Twitter: The Tanzanian government has blocked access to Twitter after hackers broke into multiple government accounts. Some of the accounts were defaced with pornography.
Turkiye busts Chinese IMSI catcher spy ring: Turkish authorities have arrested seven Chinese nationals who used IMSI catchers to spy on Uyghurs and Turkish officials. The spy ring was set up five years ago and members smuggled the IMSI catchers in the country by parts. Besides spying on Uyghurs and Turkish officials, the group also allegedly hacked into bank accounts to drain savings from locals. [Additional coverage in CNN Turk/English coverage in Middle East Eye]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview, Justin Kohler, Chief Product Officer at SpecterOps, talks to Tom Uren about the impossible challenge of managing identity directory services securely. Organizations try to implement the principle of least privilege but have no idea if they have done a good job. Justin talks about approaches SpecterOps is developing to address this problem.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
US charges Qakbot leader: The US Department of Justice has indicted a Russian national for developing and acting as the leader of the Qakbot malware group. Rustam Rafailevich Gallyamov allegedly developed the malware back in 2008 and grew it into a giant botnet. US authorities say that since 2019, Gallyamov has sold access to his botnet to at least eight ransomware crews. The DOJ has now seized $24 million worth of crypto assets linked to Qakbot operations and ransomware payments.
Teen pleads guilty to PowerSchool hack: A 19-year-old student from Massachusetts has pleaded guilty to hacking and extorting the PowerSchool education cloud platform. Matthew D. Lane admitted to stealing the personal data of more than 60 million students and 10 million teachers in a hack at the end of last year. Lane extracted a payment of $2.85 million from the company. The US Department of Justice says he also had help from other accomplices and also hacked and extorted a second unnamed company. [Additional coverage in NBC News]
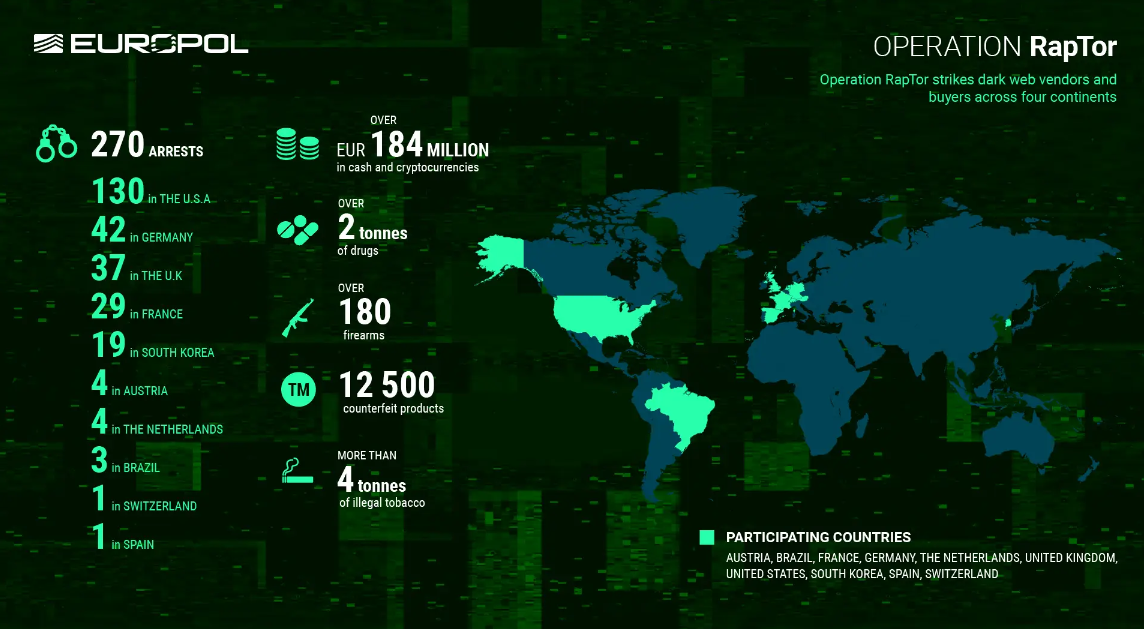
Operation RapTor: Law enforcement agencies across the world have arrested 270 suspects who sold illegal products on the dark web. The suspects were identified using data seized from dark web marketplaces Nemesis, Tor2Door, Bohemia, and Kingdom Markets. Almost half were based in the US. Authorities also seized over €184 million in cash and cryptocurrencies.
UK retail hackers identified: UK officials say the hackers who breached a set of UK retailers last month are "young" and from "the UK and histicaUS." [Additional coverage in the BBC]
AI best practices guide: CISA, the NSA, and the FBI have released a joint guide on security AI systems and their data.
Mysterious DDoS botnet: Russian security firm Curator claims to have identified and "neutralized" a giant DDoS botnet consisting of over 4.6 million infected devices. Seems to be related to this botnet.
Chinese adult-content PWA scam: C/Side researchers look at a Chinese adult-content scam campaign that uses landing pages hosted inside PWAs (progressive web apps) as a way to retain users longer and bypass basic browser protections.
TikTok malware campaign: Trend Micro has spotted a campaign using TikTok videos to lure users to piracy sites only to infect users with the Vidar and StealC infostealers.
ClickFix campaigns: Cato Networks, SentinelOne, and Trend Micro look at recent ClickFix campaigns delivering various infostealers and RATs.
Ledger Live campaign: Moonlock researchers have documented an almost year-long campaign distributing malicious versions of the Ledger Live crypto-wallet to macOS users.
DDoS prices: Cybervandals look at the evolution of DDoS-for-hire pricing over the past decade. In short, attacks are getting bigger while also becoming dirt cheap.
ViciousTrap sets up an IoT honeypot network: A threat actor has hacked over 5,500 networking devices and turned them into honeypots. The attacker, codenamed ViciousTrap, is currently monitoring devices from over 50 companies. Most of the hacked devices are deployed across Asia. Security firm Sekoia believes the attacker is trying to collect exploits and zero-days used by rival gangs.
DragonForce profile: Sophos and Quorum Cyber have published profiles on the DragonForce RaaS gang.
Malicious Chrome extensions: Earlier this week, DomainTools spotted a cluster of 100 domains advertising malicious Chrome extensions. LayerX has now identified 40+ of those extensions, some hosted on the official Chrome Store.
Malicious VSCode extensions: DataDog has found three malicious VSCode extensions that target users of the Solidity programming language. The final payload is an infostealer. DataDog linked the campaign to a threat actor (MUT-9332) that previously used VSCode extensions to deploy Monero miners.
npm packages deliver data wiper: A cluster of eight npm libraries contained malicious code designed to delete all data on infected systems. The packages were all uploaded by a suspected Chinese developer and remained undetected for almost two years. This is the second time Socket Security has found data wipers on an open-source package repository after finding a similar Go library earlier this month.

Malware technical reports
Dero cryptominer: Kaspersky looks at how the Dero cryptominer is currently attacking and infecting Docker systems that have their management APIs exposed online.
WinOS 4, Catena loader: Rapid7 has spotted a campaign they're calling the Catena loader, a complex operation that uses fake software installers disguised as popular apps like VPN and QQBrowser to deliver Winos v4.0, a hard-to-detect malware.
GhostSpy RAT: CyFirma looks at GhostSpy, an Android RAT used for banking fraud.
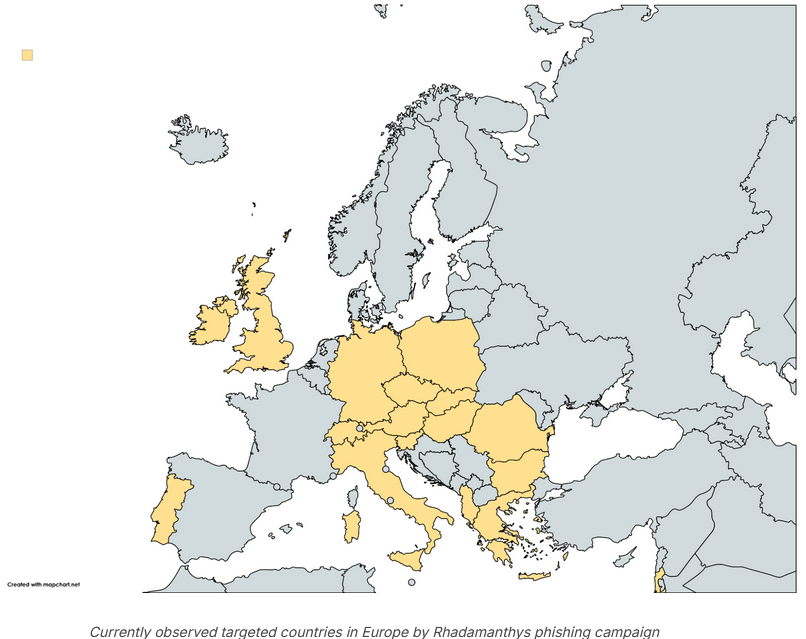
Rhadamanthys Stealer: Cybereason has published a report on a Rhadamanthys infostealer campaign targeting European users with fake copyright infringement rules.
Sponsor section
Justin Kohler, VP of Product at SpecterOps, shows how BloodHound Enterprise can be used to find and fix Active Directory (mis)configurations that could let attackers easily own your entire enterprise.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
APT28 advisory: Russia has hacked logistics firms and security cameras at border crossings and rail stations to spy on military aid sent to Ukraine. Companies in air, sea, and rail transportation have been targeted since the start of Russia's war. The attacks have been linked to unit 26165 of the GRU military intelligence services, a unit also known as APT28 or Fancy Bear. In a joint security advisory issued by 21 agencies from 11 countries, the attacks were described as unsophisticated but persistent.
TAG-110 targets Tajikistan: Recorded Future reports that a Russian APT group named TAG-110 is behind a spear-phishing campaign that targeted Tajikistan government bodies in January and February this year.
UNC5221 behind Ivanti zero-days: A Chinese APT group tracked as UNC5221 is behind recent attacks that exploited an Ivanti EPMM zero-days (CVE-2025-4427 & CVE-2025-4428). The group deployed the KrustyLoader malware on infected hosts, a malware strain they've been using for over a year. The group has a long history of developing and exploiting zero-days targeting Ivanti products. It is also known for hacking MITRE in late 2023.
UAT-6382 targets CityWorks zero-day: Cisco Talos says a group tracked as UAT-6382 has used a recent Trimble CityWorks zero-day (CVE-2025-0944) to breach local governing bodies in the US.
Silent Werewolf: Russian security firm BI.ZONE says the Silent Werewolf APT changed its malware arsenal in March. Attacks with this new malware targeted Russian and Moldovan organizations. [Post-publication update: Now, in English]
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
SharePoint Restricted View bypass: Pentest Partners have found a way to bypass Restricted View and read protected files stored on Microsoft SharePoint servers. Spoiler alert, it involves tricking an AI agent!
BadSuccessor vulnerability: Akamai researcher Yuval Gordon has published details on BadSuccessor, a privilege escalation vulnerability in Windows Server 2025 that allows attackers to compromise any user in Active Directory. BadSuccessor abuses the delegated Managed Service Account (dMSA) introduced in Windows Server 2025. The attack works against the default configuration. Gordon has published a proof-of-concept script to perform the attack after Microsoft declined to patch the issue.
Major Versa Concerto bugs unpatched: Researchers at Project Discovery have discovered three vulnerabilities in the Versa Concerto network orchestration platform. The three bugs can be chained to attack and take over Concerto instances. One of the three is an authentication bypass (CVE-2025-34027) with a severity score of 10/10. Researchers notified Versa Networks of the three issues in February, but it's unclear if patches have been released.
GitLab Duo prompt injection: Legit Security's Omer Mayraz looks at a scenario where attackers can plant malicious prompts inside source code comments and attack the GitLab Duo AI assistant to leak source code or perform other malicious actions.
FortiVoice zero-day write-up: Horizon3 researchers have published a technical analysis of CVE-2025-32756, an actively exploited zero-day in FortiVoice phone systems.
Invati EPMM zero-days write-up: Profero has published a technical analysis of two Ivanti zero-dayz exploited in the wild (CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428).
Denodo Scheduler RCE: Rhino Security has published a write-up of CVE-2025-26147, a post-auth RCE in Denode Scheduler.
Netwrix Password Secure RCE: 8Com has published a write-up of CVE-2025-26817, a post-auth RCE in Netwrix Password Secure, an enterprise password manager.
Samlify signature wrapping attack: The Samlify Node.js authentication library has released a security fix to patch a signature wrapping attack that could have been used to bypass SAML SSO authentication (CVE-2025-47949).
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released ten security advisories for various products.
Huge backlash against GitHub's Copilot integration: Hundreds of users are demanding that GitHub add an option to block issues and pull requests made using the company's new Copilot AI agent. The new feature was announced on Monday and works via a dedicated GitHub user that cannot be blocked. Developers say the Copilot agent is already flooding their projects with AI junk that's wasting their time. [Additional coverage in Socket Security]
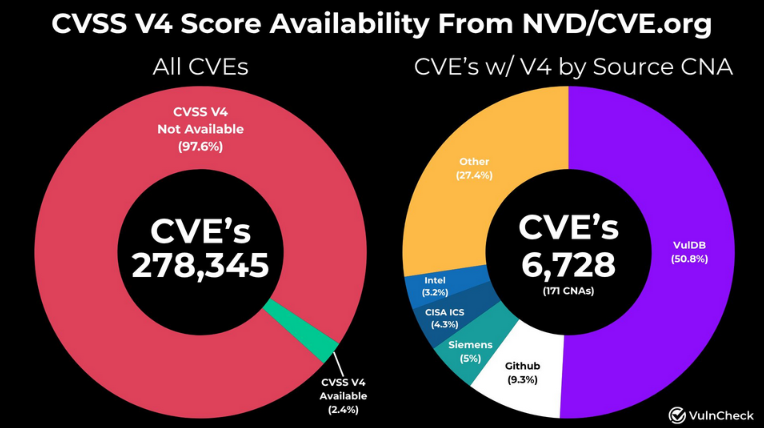
CVSSv4 progress: According to VulnCheck researcher Patrick Garrity, only 2.4% of all CVEs have a CVSSv4 score 1.5 years after the standard passed. Around 1.2% of those scores are from one CNA, so it's safe to say the standard is dead right now.
"As vulnerability management teams consider whether to adopt CVSS v4, they're confronted with a tough reality: there is little incentive for CNAs to migrate to v4 or back-score existing CVEs, rendering the newer standard relatively useless for prioritization purposes at this time."
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Arctic Wolf, AU10TIX, Corrata, Firefox, Huntress, SANS, Snyk, Thales, and Trustwave have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
New tool—EvilWorker: Antoine Hazebrouck has released EvilWorker, a new AiTM attack framework based on service workers.
HOPE conference update: The HOPE security conference has sold 50% fewer tickets this year as speakers and attendees are afraid to travel to the US due to the Trump crazy immigration crackdown that keeps detaining foreigners with valid travel visas. [Additional coverage in 404 Media]
Botconf 2025 videos: Talks from the Botconf 2025 security conference, which is taking place this week, are now available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about how Telegram took down the two largest ever criminal marketplaces recently. The pair discuss why Telegram is now cooperating with authorities after historically being reluctant and whether this assistance will continue.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq examine what makes it hard for even competent hackers to contribute to state-backed espionage agencies.
