Risky Bulletin Newsletter
February 28, 2024
Risky Biz News: US sanctions Sandvine over Egypt sales
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by no-code automation platform Tines. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

The US Commerce Department has sanctioned Canadian company Sandvine for providing internet mass surveillance technology to the Egyptian government.
In a press release, US government officials said Sandvine's networking equipment was used to monitor and censor internet traffic in Egypt and target local political figures and human rights activists.
Sandvine Canada and five of its subsidiaries were added to the Commerce Department's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) Entity List.
American companies are prohibited from selling technology to Sandvine without a license from the US government—which BIS has rarely given out, operating under a "presumption of denial" review policy.
Sandvine becomes the fifth surveillance and spyware vendor to be added to the agency's Entity List. BIS previously sanctioned Candiru, NSO Group, Intellexa, and Cytrox in 2021 and 2023.
Sandvine was founded in 2001 and is known for its network traffic-shaping technology. Its most successful products provide network congestion and deep-packet inspection capabilities.
The company's problems started appearing in the late 2010s when human rights advocacy groups and security researchers started raising the alarm about Sandvine gear consistently appearing in oppressive regimes.
A Bloomberg 2020 report linked Sandvine equipment to internet censorship efforts in 15 countries—Algeria, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Egypt, Eritrea, Jordan, Kuwait, Pakistan, Qatar, Russia, Sudan, Thailand, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, and Uzbekistan.
A CitizenLab report from September of last year claimed that Sandvine equipment was used to deliver the Predator spyware to the phone of Ahmed Eltantawy, an MP who was trying to mount a presidential campaign.
CitizenLab says the traffic injection technique is similar to how Sandvine equipment was used in Turkey to deliver government spyware to hundreds of users in 2018.
Even before this week's US sanctions, the company has been under immense pressure for its repeated sales to oppressive regimes. The company pulled out of Belarus in 2020 after the Lukashenko regime used Sandvine equipment for internet shutdowns and censorship in the aftermath of fraudulent elections.
The company also pulled out of the US market last year after getting the hint it wasn't welcome over its long history of working with authoritarian regimes.
The latest Sandvine trade restrictions are part of a larger US crackdown on commercial surveillance and spyware vendors that have a history of facilitating repression and enabling human rights abuses. Earlier this month, the US State Department restricted visas for individuals involved in the development and misuse of commercial spyware.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Blueberry Protocol cyber-heist: The operators of the Blueberry DeFi platform paused transactions after a hacker stole $1.35 million worth of assets. Blueberry says the hacker used an exploit in one of its contracts to drain funds from its wallets. The company says it has already refunded 80% of the stolen funds to affected users. Blueberry plans to relaunch operations this week.
Change Healthcare incident: The AlphV ransomware gang is behind the cyberattack that crippled the operations of pharmacies across the US last week. The incident impacted Change Healthcare, a prescriptions and payments processing platform operated by UnitedHealth. The revelation comes to contradict the company's statements that the incident was the work of a nation-state threat actor. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
MGM investigation: MGM Resorts says it's facing state and federal investigations in connection to its 2023 security breach. [Additional coverage in CybersecurityDive]
Hamilton cybersecurity incident: The city of Hamilton in Canada is dealing with a cybersecurity incident.
Oakley ransomware attack: The city of Oakley in California is dealing with a ransomware attack.
Hesse ransomware attack: The German state of Hesse says its federal systems were hit by ransomware in an incident that took place last week. The incident impacted telephone, email, and server infrastructure, most of which have already been restored.
Matthew Perry account hack: Hackers have taken over the Twitter account of deceased Friends star Matthew Perry and promoted a fake foundation set up in his name to collect donations. [Additional coverage in Sky News]
General tech and privacy
Tails 6.0: The Tor Project has released v6.0 of the Tails operating system. The latest OS version comes with protection against malicious USB devices, dark mode support, better Gmail support, and more.
AI used in warfare: The US Central Command has allegedly already used AI technologies on the battlefield—namely to narrow down places to bomb in Yemen. [Additional coverage in Benzinga]
LinkedIn complaint: Multiple European privacy organizations have filed a complaint against LinkedIn in the EU for using sensitive personal data to serve ads on the platform. The organizations claim LinkedIn used information such as race, political opinions, and sexual orientation to serve ads. The use of such sensitive information is against the EU's Digital Services Act.
Government, politics, and policy
White House call for memory safety: The White House has called on the private sector to increase the adoption of memory-safe programming languages. The White House becomes the third major US government institution to urge developers to use safer programming languages. CISA and the NSA made similar calls at the end of last year. The initiative is meant to reduce the number of vulnerabilities in modern software caused by memory management-related bugs.
DOE cybersecurity investments: The US Department of Energy has announced a $45 million investment in 16 cybersecurity-related projects. [Additional coverage in CyberScoop]
Meta establishes EU disinformation team: Social media giant Meta has set up a special team to tackle disinformation campaigns targeting the EU ahead of this year's continent-wide EU Parliament elections.
New Australian cyber coordinator: The Australian government has named Lieutenant General Michelle McGuinness as its next national cyber security coordinator. She replaces Air Marshall Darren Goldie, who was recalled last year. General McGuinness served in the Australian Defence Force for 30 years. She recently served as a liaison with the US Defense Intelligence Agency. [Additional coverage in itNews]
Calls for a revenge porn law in Albania: A non-profit organization has asked the Albanian government to criminalize revenge porn after two women took their lives this year after their sexually explicit photos were leaked online. [Additional coverage in Euronews]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Tines co-founder and CEO Eoin Hinchy about how the unique features of AI and ML algorithms are more suited to blue teamers and defending networks rather than attackers.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Former cop charged for hacking: US authorities have indicted a former New Jersey cop on hacking-related charges. Ayron Taylor allegedly hacked into the social media accounts of at least 20 women. Officials say Taylor sent sexually explicit photos the victims took of themselves to their Facebook and Snapchat contacts. Taylor faces 97 charges, including for distribution of child pornography. [Additional coverage in News12]
Cyber Threat 2023: France's CERT has published its yearly Cyber Threat Overview for last year. The report deals with cybersecurity incidents and threats in France last year.
Fake wallet apps: China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has published a warning about the proliferation of fake wallet apps for the country's central banking digital currency (CBDC).
Chinese cybercrime ecosystem: SpyCloud Labs has published an analysis and webinar on the Chinese hacking underground.
Cybercrime in Russia & CIS: Russian security firm FACCT has published a report looking at the cybercrime and threat ecosystem impacting Russia, Belarus, and the rest of CIS. According to FACCT, the "majority of cyber attacks in Russia in 2023 were politically motivated." The company says it's currently tracking 14 major nation-state groups. [Additional coverage in The Record]
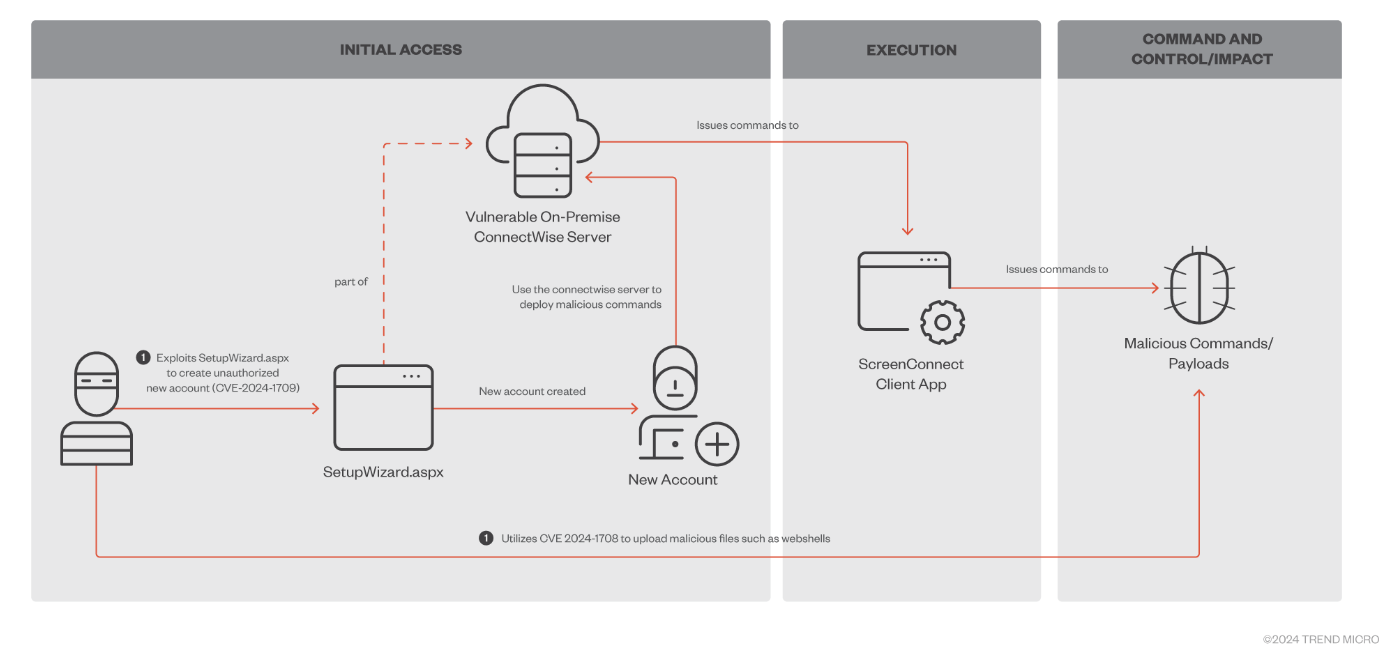
ScreenConnect attacks: The BlackBasta and the Bl00dy ransomware gangs are now exploiting two recently disclosed ScreenConnect vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-1708 and CVE-2024-1709) to breach networks and encrypt files. Trend Micro says the two are among the many threat actors that are currently exploiting the two vulnerabilities. ConnectWise disclosed and released patches for the two issues last week. Active exploitation started a day after the patch.
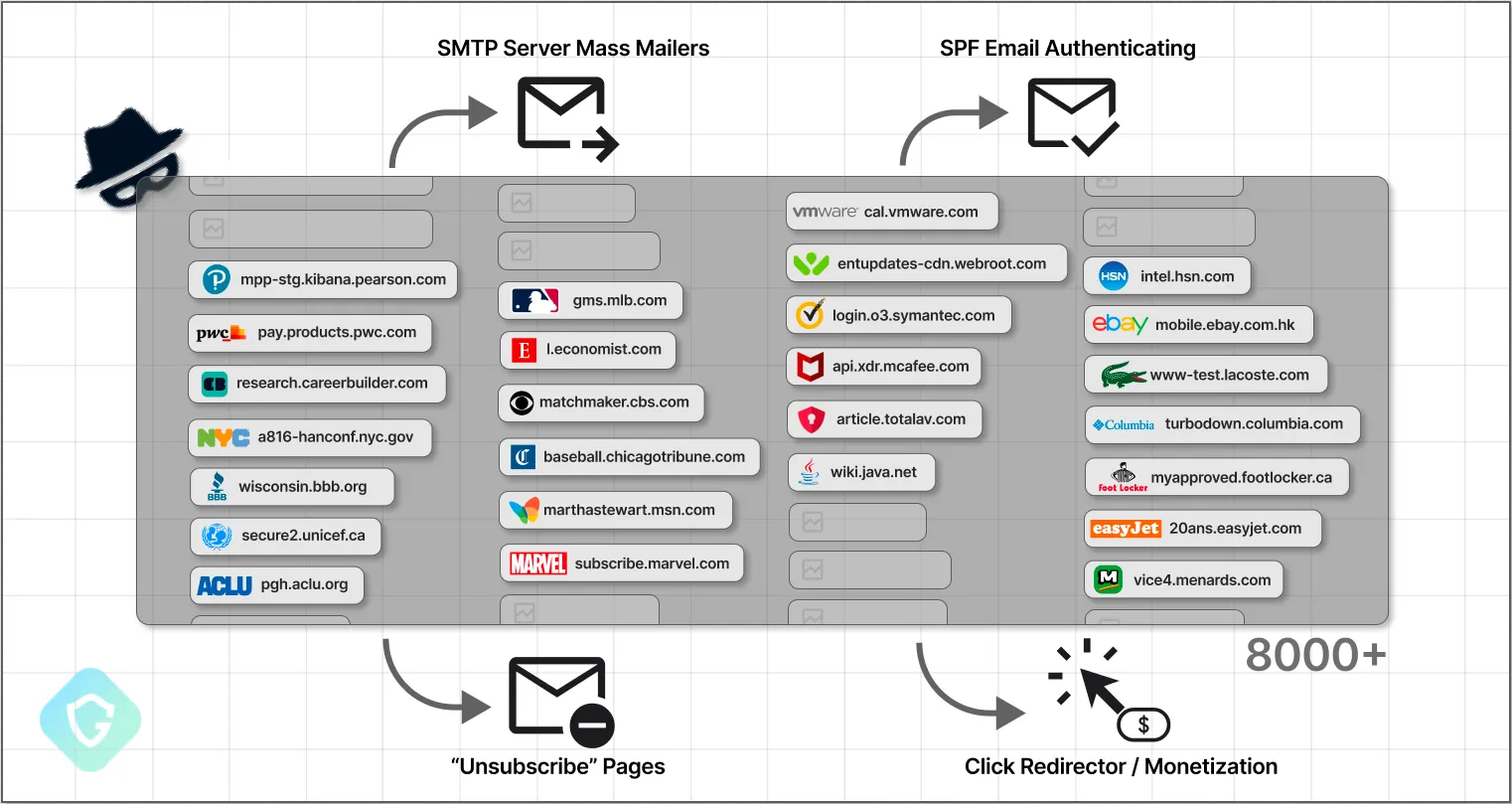
SubdoMailing: A threat actor named ResurrecAds has hijacked more than 13,000 subdomains for email spam and phishing operations. Some of the hijacked subdomains belong to some of the world's largest brands, such as eBay, CBS, VMware, McAfee, UNICEF, and others. Guardio Labs says ResurrecAds uses a technique they named SubdoMailing to hijack subdomains and abuse them to send malicious emails. The company says ResurrecAds has been operating for more than a year and is currently sending more than 5 million emails per day.
Malware technical reports
Xeno RAT: CyFirma researchers look at Xeno RAT, an advanced remote access trojan that has been available on GitHub for a few months now.
Nood RAT: AhnLab has published a report on Nood RAT, a new Linux RAT that researchers think it was based on the Gh0st open-source RAT.
DCRat: ANY.RUN researchers have published a technical analysis of DCRat, a remote access trojan that's been observed in the wild since 2018.
Atomic Stealer: Bitdefender has discovered a new version of the Atomic Stealer in the wild. Also known as AMOS, Atomic is an infostealer that targets macOS platforms. It was first spotted in attacks last year and is part of a wave of malware targeting macOS users as of late.
TimbreStealer: Cisco Talos has a report out on TimbreStealer, a new infostealer used in recent campaigns targeting Mexican users. The infostealer seems to have been used in the wild since November 2023.
Agent Tesla: Forcepoint researchers have published a report on the good ol' Agent Tesla infostealer.
Abyss Locker: Fortinet researchers analyze Abyss Locker, a new ransomware strain that is based on the leaked source code of the HelloKitty ransomware. The current version can run on both Windows and VMware ESXi systems.
SWIFT ransomware: A Chinese malware researcher going by the name of Panda Zhengzheng has published an analysis of the new SWIFT ransomware.
LockBit ransomware: ShadowStackRE has published a technical podcast on this little-known ransomware strain nobody has ever heard of named LockBit.
Gootloader: The DFIR Report team looks at one of the bazillion SEO poisoning campaigns that are currently inundating the internet. This one, in particular, used poisoned search results to trick users into downloading software infected with Gootloader.
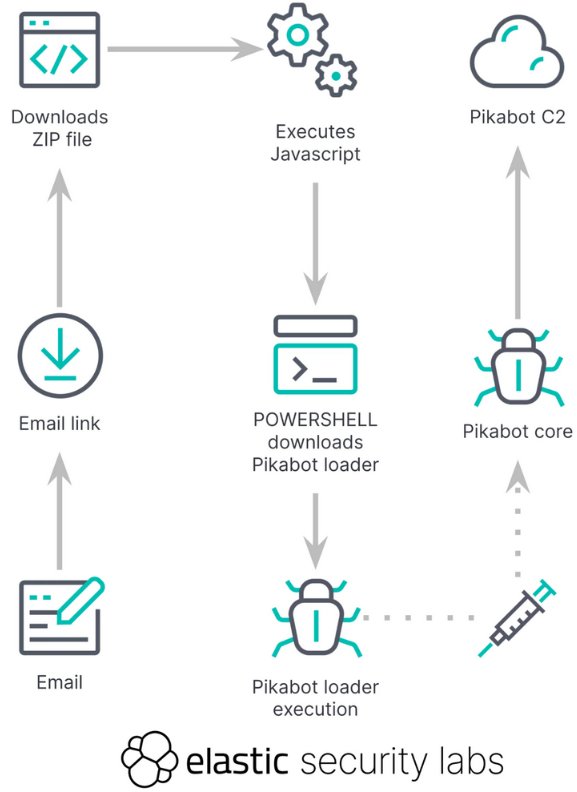
PikaBot: Elastic's security team has published a report on the latest changes to the PikaBot malware. Zscaler published a report on the same PikaBot updates earlier this month.
Sponsor Section
In this demo, Tines CEO and co-founder Eoin Hinchy demonstrates the Tines no-code automation platform to RiskyBiz host Patrick Gray.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
SVR initial cloud access: Five Eyes cyber agencies have published a joint advisory covering the most common techniques used by SVR cyber-espionage group APT29 to gain initial access to cloud environments.
APT28's Moobot: The FBI has published an industry alert [PDF] on APT28's use of Ubiquiti Edge OS-based routers (aka EdgeRouters) for the Moobot botnet. US authorities took down the botnet earlier this month.
UAC-0184: Morphisec looks at UAC-0184, a threat actor that has been using IDAT Loader to target Ukrainian organizations in Finland.
UAC-0149: Ukraine's CERT team says that a threat actor it tracks as UAC-0149 has attempted to infect some of the country's military personnel with malware. The attacks began in late 2023 and have used Signal spear-phishing. The final payload is a PowerShell-based malware strain tracked as COOKBOX.
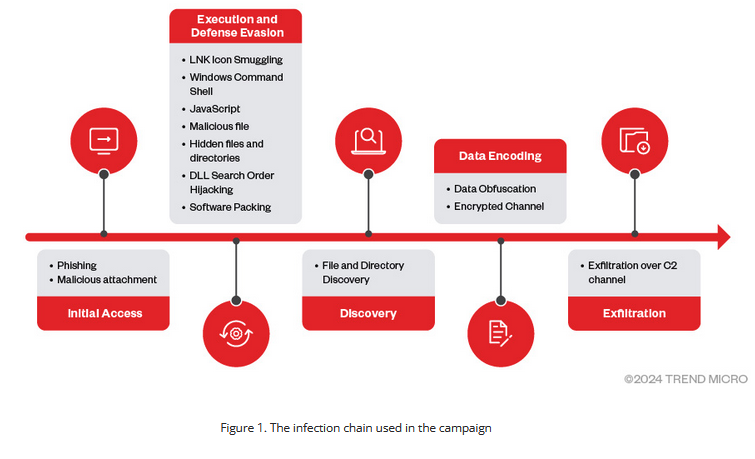
Earth Lusca: Trend Micro says there is an overlap between the recent leak at Chinese hacker-for-hire company i-SOON and past cyber-espionage operations linked to the Earth Lusca APT. The overlap includes i-SOON cyber tools and lists of past victims. Trend Micro says some past i-SOON victims were also victims of past Earth Lusca attacks. A security researcher known as Natto Thoughts also linked i-SOON to Earth Lusca activity in October of last year, months before the leak. Trend Micro says recent Earth Lusca operations targeted Taiwan ahead of its recent elections.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
GWL vulnerability: Security researcher Jan Kopriva has published details about an open-redirect vulnerability in Google's Web Light service.
VMware security update: VMware has published a security update for Fusion and Workstation products.
Infosec industry
New tool—Shelter: Security engineer Kurosh Dabbagh Escalante has open-sourced Shelter, a tool that uses a sleep obfuscation technique to fully encrypt in-memory payloads.
New tool—VulnCheck KEV: Security firm VulnCheck has launched VulnCheck KEV, their own version of the CISA KEV database. The VulnCheck KEV database contains a list of vulnerabilities that VulnCheck has seen exploited in the wild. It contains more than 1,900 entries, with 876 more entries than what CISA KEV tracks.
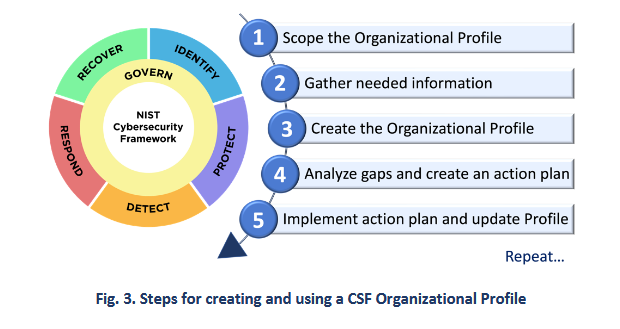
NIST CSF 2.0: US NIST has released version 2.0 [PDF] of its Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). The original NIST Cybersecurity Framework was released in 2014. It was a voluntary document that contained guidance on how to secure IT networks. Version 2.0 is a much-needed facelift that updates threat models for new threats, such as supply chain risks. CSF 2.0 was also designed to cover a broader scope of organizations beyond critical infrastructure operators.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq apologize for repeating a quote that is purported to be Russian cyber doctrine but is not. They also wonder why this phenomenon has happened before with the so-called Gerasimov doctrine.

