Risky Bulletin Newsletter
February 19, 2024
Risky Biz News: New NSO Group capability revealed in court documents
Written by

News Editor
This newsletter is brought to you by asset inventory and network visibility company runZero. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

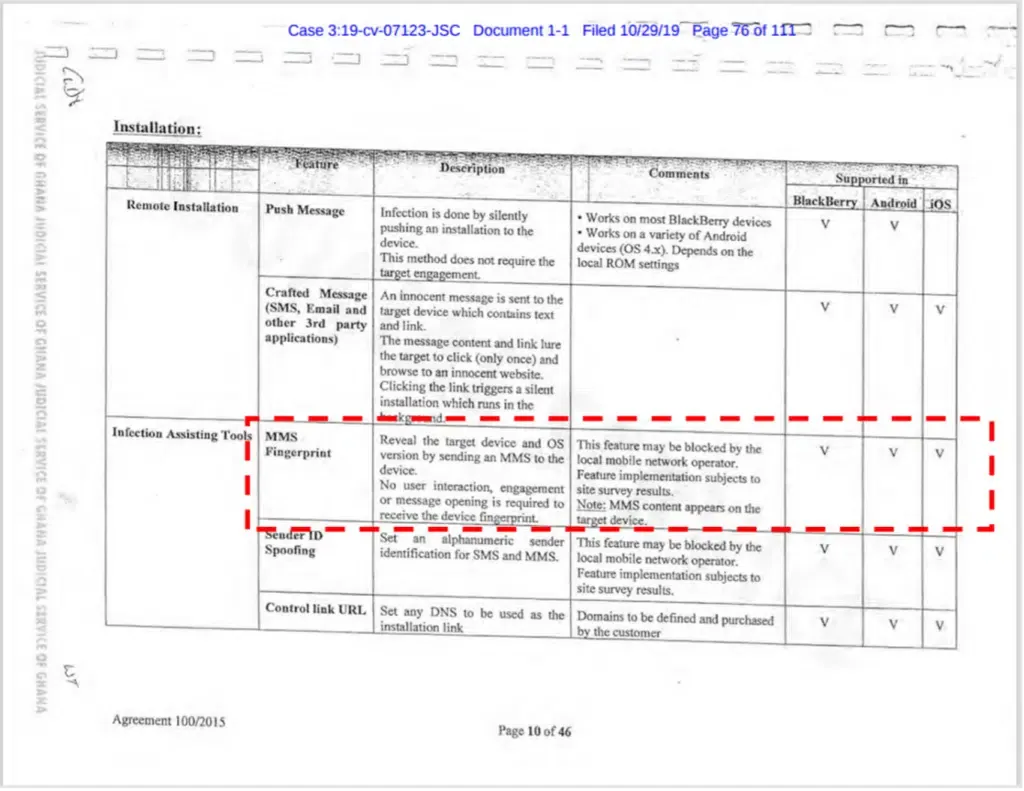
ENEA, a Sweden-based telecom security firm, claims it reproduced a user fingerprinting technique advertised and sold by Israeli spyware vendor NSO Group.
Named MMS Fingerprinting, the technique can collect information on a target's smartphone and operating system just by sending an MMS message.
NSO Group claims no user interaction is needed besides knowing the target's phone number.
ENEA says that it learned about this technique after reading court documents filed by WhatsApp in 2019 in its lawsuit against NSO Group—with MMS Fingerprinting being mentioned in a contract between an NSO reseller and Ghana's telecom regulator.
A CTO Cathal McDaid says that NSO's surveillance capabilities were largely known in the telecom industry at the time of the lawsuit, this technique was not.
McDaid says that after an analysis of the MMS standard, his company believes it identified how this attack works.
He says the issue comes with the design of the MMS standard itself, which was created in an era before capable smartphones. While called MMS, the standard also utilizes SMS messages during its multi-step process of sending a multimedia message (MMS, aka an SMS with images or videos attached).
McDaid says that for the process of notifying a receiving user that there is an MMS waiting to be downloaded from their telco's servers, the telco will send out a "silent SMS" (or a Binary SMS) message to the recipient. These silent SMS messages would query a user's device to see if their (not-yet-smart)phone was capable of handling MMS content. Since the messages had purely an ephemeral role, they would not show in the user's SMS inbox.
ENEA says that while this technique may not need any user interaction and may be hard to spot, it can be blocked on mobile networks quite easily—if networks have not phased out MMS altogether.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Duelbits crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen $4.6 million worth of crypto-assets from crypto gambling platform Duelbits. The attacker is believed to have compromised a private key and gained access to one of the platform's hot wallets. The hacker laundered the stolen funds immediately after the theft.
LINE data breach: Ly Corp has published more details about its November 2023 data breach. The company has blamed the breach on a NAVER employee getting his work PC infected with malware. NAVER is one of Line's cloud providers. [h/t piyolog]
Wyze security issue: Smart home product maker Wyze dealt with an outage the company described as a "possible security issue" that impacted login and connectivity to some of its devices.
Romanian hospitals attack: Romania's cybersecurity agency has linked a ransomware attack that impacted 100 hospitals across the country to a ransomware strain named Backmydata, a variation of the larger Phobos ransomware family—which had its source code leaked online years ago. It also released IOCs from the attack.
General tech and privacy
New Chrome security feature: Google is adding a new security feature to Chrome that will detect websites scanning a user's local network. The new feature is named Private Network Access and will ship with Chrome 123, scheduled for release in mid-March. The feature can be used to detect malicious websites that try to modify settings on local routers and other smart devices. This technique is known as drive-by pharming or SOHO pharming and has been used by some malware botnets. The feature will initially ship in Chrome in a warning-only mode. There are plans to have Chrome block requests from the internet to private networks in the future.
Signal 7 beta: The first beta version of Signal 7.0 is out. This is the first Signal app version that supports usernames instead of phone numbers as user IDs.
Twitter's bot problem: Bot detection platform CHEQ has found that almost three-quarters of web traffic originating from Twitter/X during the Super Bowl LVIII week came from bots. [Additional coverage in Mashable and from Olivier Simard-Casanova]
Mastodon spam attack: Mastodon servers saw a coordinated spam attack over the weekend.
Government, politics, and policy
Munich Cyber Security and Security Conference: The Record has good coverage of the major talking points from this year's edition of the Munich Cyber Security and Security Conference.
ABA comes out against commercial spyware: The American Bar Association has urged the US government to adopt a moratorium on the sale, purchase, transfer, servicing, and use of commercial spyware from abusive vendors. The organization has urged authorities to adopt an international framework to regulate the industry and protect human rights. The agency's statement comes a week after US authorities announced travel visa restrictions for individuals linked to commercial spyware abuses.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Rob King, runZero’s Director of security research. The pair talk about the world of Operational Technology protocols and how Rob dissects these protocols to be sure that active discovery of OT devices is safe.

Try runZero for free at https://www.runzero.com/try/signup/
Cybercrime and threat intel
Zeus/IcedID member pleads guilty: A Ukrainian national has pleaded guilty to his role in two separate major malware operations. Vyacheslav Igorevich Penchukov served as a leader in the Zeus malware gang in the late 2000s and then worked with the IcedID gang in the late 2010s. Penchukov was charged in 2014 for his role in the Zeus gang and added to the FBI's Cyber Most Wanted list. He was arrested in Switzerland in 2022 and extradited to the US in 2023.

Racoon Stealer dev extradited: US authorities have extradited a Ukrainian national named Mark Sokolovsky in relation to his alleged role in creating and selling the Raccoon Stealer malware. Sokolovsky was arrested in the Netherlands in March 2022 after authorities seized and shut down his operation. Until US authorities announced his arrest months later, fellow malware developers thought Sokolovsky had died in the war in Ukraine. Sokolovsky has spent the last two years fighting his extradition, claiming that US authorities would treat him inhumanely and violate his human rights—claims a Dutch judge disagreed with.
Aladdin hacker gets no prison time: A South Korean court ruled that an 18-year-old student who hacked the Aladdin e-book platform should be trialed as a child in a juvenile court and avoid any prison time. The student was accused of hacking the platform in June of last year, stealing and leaking e-books, and attempting to extort Aladdin for $2.7 million in Bitcoin. The prosecution has filed an appeal against the court's decision. They argue the student planned the hack in advance with two accomplices and that there is a high risk the teen will repeat his offense if there is no severe punishment. [Additional coverage in Kyunghyang Shinmun]
AstroStress admin charged: US authorities have charged a Los Angeles man for allegedly running DDoS-for-hire platform AstroStress. Scott Esparza was charged 14 months after authorities took down the site and detained his associate in December 2022. Officials say Esparza allegedly worked with Shamar Shattock of Florida to run the service. AstroStress allegedly had thousands of registered users and was used to launch millions of DDoS attacks. [Additional coverage in The Record]
AlphV reward: The US State Department is offering a $10 million reward for information on administrators of the AlphV ransomware operation. Officials are also offering a $5 million reward for information on individuals attempting to participate in AlphV attacks. The AlphV group started operations in December 2021 and is believed to have spun off from the DarkMatter gang. Authorities disrupted AlphV's server infrastructure in December of last year, but the group was back up and running a month later.

Variston is losing staff: Barcelona-based spyware maker Variston has allegedly lost half of its staff after a disgruntled former employee shared the company's browser hacking tools with Google back in 2022. Because Google kept exposing its exploits and operations, the company is now allegedly shutting down—according to some unconfirmed leaks from former staffers. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
CISA IR report: CISA and MS-ISAC have published an IR report from an incident at a state government organization where attackers gained access via a former employee's account.
New npm malware: Twelve malicious npm packages were discovered last week. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for more details.
New ransomware: Broadcom has spotted a new ransomware in the wild named JKwerlo. It is written in Go and is currently used in malspam campaigns targeting Spanish and French-speaking users.
App security report: CrowdStrike has published its yearly State of Application Security report.
YoMix service linked to DPRK money laundering: Almost a third of all funds that entered the YoMix Bitcoin mixing service came from wallets associated with cryptocurrency hacks. Blockchain analysis service Chainalysis says that many of these funds came from wallets associated with North Korean hackers. YoMix has become North Korea's favorite crypto laundering service after US authorities sanctioned Tornado Cash and Sinbad in previous years. Chainalysos says that ransomware gangs preferred crypto-gambling and crypto bridge platforms when it came to laundering their profits last year..
Malware technical reports
SocGolish: ReliaQuest looks at a new Python script used by the SocGolish group for persistence on infected hosts.
ISFB Loader: Egyptian malware analyst Mohamed Talaat has published a technical analysis of the old ISFB/Gozi Loader.
DarkVNC: eSentire analyzes DarkVNC, a VNC-based utility used by multiple cybercrime groups to access compromised systems. The tool has been available for sale on underground hacking forums since November 2016.
Spynote: Fortinet researchers have published a technical report on Spynote, an Android RAT that was first spotted back in 2020 and which recently added support for stealing crypto-wallet data.
Warzone RAT: The FBI has released a technical report [PDF] on Warzone RAT, a malware operation they disrupted two weeks ago.
SNS Sender: SentinelOne's Alex Delamotte looks at SNS Sender, a script that enables bulk SMS spamming using AWS SNS. The script has been used for some smishing operations and is often deployed on hacked AWS SNS instances.
RansomHouse's MrAgent: Trellix has analyzed MrAgent, a tool created by the RansomHouse group to help its members automate the deployment of its ransomware on VMWare ESXi instances.
Alpha/MyData ransomware: Symantec has found similarities between the new Alpha ransomware and the defunct Netwalker operation. Also known as MyData, the new Alpha gang began operations in February 2023, almost two years after authorities took down Netwalker. Researchers believe the new Alpha RaaS may have purchased the old Netwalker source code or may include former Netwalker coders.
Sponsor Section
Senior Sales Engineer Ali Cheikh demonstrates the runZero platform to Risky Business host Patrick Gray. runZero is a cyber asset management tool that combines active scanning, passive discovery, and API integrations to discover IT, OT, and IoT assets (both managed and unmanaged) across your network, including cloud, mobile, and remote environments.
Try runZero for free at https://www.runzero.com/try/signup/
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Kimsuky: AhnLab looks at a Kimsuky campaign targeting South Korea and delivering the TrollAgent infostealer. [Later edit: Now in English.]
Navalny-related bot spam: Pro-Russian bot networks are spamming VK and Twitter with misinformation surrounding Alexei Navalny's death, trying to blame his death on a blood clot formed during a hunger strike in early 2021. In the meantime, Russian authorities are doing everything possible to hide his body.
Midnight Blizzard Microsoft hack: Cisco's Splunk has published an analysis of how the Midnight Blizzard Russian APT breached Microsoft's infrastructure. Similar reports are also available from SpecterOps and Wiz.
TAG-70: A Russo-Belarusian cyber-espionage group tracked as TAG-70 has targeted more than 80 organizations in a campaign that took place last year between October and December. The most notable targets included the Embassy of Iran in Moscow, the Embassy of Iran in the Netherlands, and the Embassy of Georgia in Sweden. According to Recorded Future, the group used multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the Roundcube webmail client to gain access to victims' inboxes (likely CVE-2020-35730 and CVE-2023-43770). TAG-70 overlaps with activity reported by other security firms as Winter Vivern, TA473, and UAC0114.
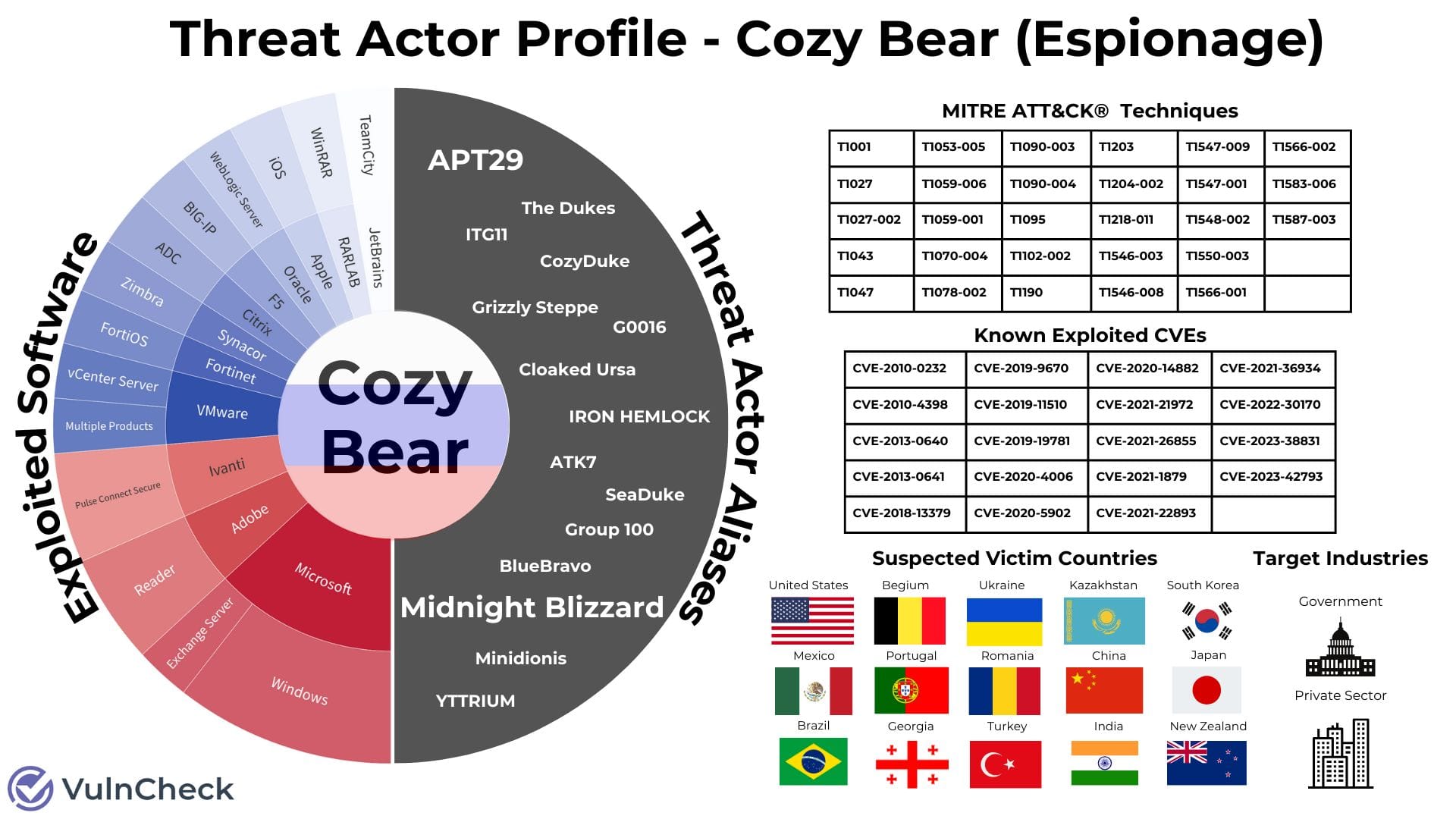
Cozy Bear: VulnCheck's Patrick Garrity has put together a visualization of Cozy Bear's most commonly used techniques and vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Mastodon RCE: Software engineer Arcanicanis has published a technical write-up on CVE-2024-23832, a Mastodon bug patched earlier this month that can allow user account takeovers.
Kubernetes security updates: Google has shipped two security updates for Kubernetes.
MonikerLink PoC: Public proof-of-concept code is now available MonikerLink (CVE-2024-21413), a Microsoft Outlook RCE.
AMD PSD misconfigurations: IOActive researchers have found that vendors like Acer, Lenovo, and Huawei are shipping devices with a misconfigured AMD Platform Secure Boot (PSB). For some devices, AMD PSB is not turned on by default, but it's still misconfigured either way.
Android security updates study: Google analyzed the timing of more than 367,000 Android security updates shipped to ~600 different smartphone models between 2014 and 2023 and found that vendors still have a long way to go to deliver timeline updates.
Ivanti 2021 bug: Security firm GreyNoise has discovered that a vulnerability patched in the Ivanti product in 2021 was actually an intentional backdoor in one of the software's open-source libraries. The backdoor resided in CSRF-magic, a PHP library for securing applications against cross-site request forgery attacks. Even if the backdoor was publicly exposed in 2016, Ivanti was still using the library for its EPM Cloud Services Appliance (CSA) appliance. When Ivanti fixed the issue, it told described the patch as a "code injection" vulnerability (CVE-2021-44529) instead of what it actually was—a backdoor.
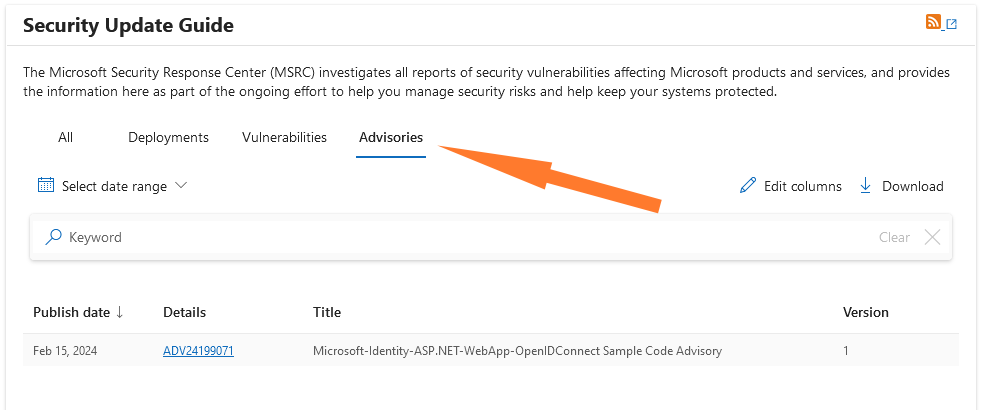
MSFT security advisories: Microsoft has updated its Patch Tuesday portal—known as the Security Update Guide—to add a new tab named Advisories. The company says this new tab will contain information on cybersecurity issues that need to be addressed but are not eligible for a CVE identifier. The first advisory was published last week and asked developers to review their Azure apps if they copied code from one of Microsoft's sample apps. Microsoft says the sample app is vulnerable to a remote code execution attack.
Infosec industry
Tool update—IDA: ID: Hex-Rays has released v8.4 of IDA.
Tool update—DFIR PowerShell: Security engineer Bert-Jan Pals has updated DFIR PowerShell to v2. This is a collection of PowerShell scripts that can help you respond to cyber attacks on Windows systems.
New tool—OpenGFW: The Aperture Internet Laboratory has released OpenGWF, an attempt to reproduce the technology behind China's Great Firewall.
New tool—Magika: Google has open-sourced a tool named Magika, an AI-powered system that can be used to detect binary and textual file types.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about what up-and-coming countries should expect from a Cyber Command and whether they should invest in it.

